Business financial planning is the strategic roadmap that guides your company's financial future. It’s the process of setting clear financial goals, allocating resources wisely, and making informed choices to steer your business toward long-term stability and growth. Think of it as the map and compass for your entire operation.
What Is Business Financial Planning, Really?
Forget the image of rigid accounting tasks and endless spreadsheets. At its core, business financial planning is about being the captain of a ship, purposefully navigating toward a destination. It’s a proactive strategy, not a reactive chore. Without this strategic guidance, a business is simply drifting, susceptible to every economic storm and unexpected current.
A solid plan is your primary tool for anticipating challenges before they arise and seizing opportunities the moment they appear. It ensures every rand spent, every investment made, and every new hire aligns with your ultimate vision. This process turns abstract goals into concrete, actionable steps.
Moving Beyond Basic Bookkeeping
Many business owners confuse day-to-day bookkeeping with true financial planning. While accounting looks backward to record what has already happened, financial planning looks forward to dictate what will happen.
- Bookkeeping is about historical accuracy—tracking transactions and ensuring the books are balanced.
- Financial Planning is about future strategy—using that historical data to make projections, set budgets, and guide decisions.
This distinction is crucial. Simply knowing how much money you made last quarter is useful, but a financial plan helps you decide how to increase that figure by 20% over the next year.
Business financial planning is less about counting money and more about making money count. It provides the framework to connect your daily operations with your long-term ambitions, ensuring your business not only survives but thrives.
Why It Is Critical for South African Businesses
In a dynamic economic landscape like South Africa’s, a robust financial plan becomes a critical survival tool. For instance, managing cash flow effectively is paramount for local businesses facing volatile income streams and rising operational costs that can disrupt continuity. Experts suggest that adopting real-time tools to monitor liquidity and prioritise collecting outstanding payments is essential for stability. You can explore more insights about financial lessons for South African entrepreneurs from Maverick Accountants.
Ultimately, business financial planning demystifies your company's finances. It empowers you to understand the "why" behind the numbers, giving you the confidence to lead decisively, invest smartly, and build a resilient enterprise capable of weathering any economic climate.
The Core Pillars of Your Financial Strategy
 A solid financial plan isn’t just a single document you create once and file away. It’s a living strategy built on three core pillars that work in harmony to keep your business stable and poised for growth.
A solid financial plan isn’t just a single document you create once and file away. It’s a living strategy built on three core pillars that work in harmony to keep your business stable and poised for growth.
Think of it like building a house. You need a foundation, walls, and a roof. Miss one, and the whole structure is compromised. Let's break down these essential components to see how they fit together.
Budgeting and Forecasting: The Blueprint
First up is budgeting and forecasting. This is the architectural blueprint for your financial house, mapping out where every rand should go and what the finished structure might look like. A budget is your immediate spending plan, while a forecast is your educated guess about what’s coming down the road.
A budget isn’t about penny-pinching; it's about being intentional. It’s a tool that helps you steer your capital towards the things that create real value, whether that’s a killer marketing campaign, developing a new product, or hiring top talent.
Forecasting, on the other hand, is your crystal ball. By looking at past performance and current market trends, you can predict future sales, estimate upcoming costs, and brace for seasonal shifts. A retailer, for instance, would use forecasting to anticipate the festive season rush, allowing them to budget for extra stock and staff well in advance.
A budget tells your money where to go instead of you wondering where it went. Forecasting gives you a glimpse into the future, so you can prepare for it today. Together, they form the proactive core of your financial planning.
Cash Flow Management: The Lifeblood
The second pillar, and arguably the most critical, is cash flow management. If budgeting is the blueprint, cash flow is the plumbing and electricity—the essential systems that keep everything running day-to-day. It’s absolutely vital to understand this: profit and cash are not the same thing. A business can be profitable on paper and still go under because it runs out of cash.
Profit is what’s left after you subtract expenses from revenue. Cash flow, however, is the actual movement of money in and out of your bank account. You might close a huge deal (profit!), but if your client takes 90 days to pay, you have no cash from that sale to cover salaries or pay suppliers next week. This is precisely how otherwise healthy businesses get into trouble. In fact, a U.S. Bank study found that a staggering 82% of business failures are due to poor cash management.
Good cash flow management boils down to a few key activities:
- Tracking your receivables: Making sure customers pay you on time.
- Managing your payables: Paying your own bills strategically without souring relationships with suppliers.
- Keeping a cash reserve: Having a safety net for unexpected expenses or a slow month.
For businesses that work with international clients, optimising cross-border payments becomes a huge part of managing cash flow. Traditional banking delays and high fees can strangle liquidity. This is where modern payment solutions, which offer faster transfers and better exchange rates, can give you a serious strategic edge.
Risk Management: The Insurance Policy
The final pillar is risk management. This is your insurance policy, fire alarm, and security system all rolled into one. It’s all about spotting potential financial threats and having a plan to defuse them before they turn into full-blown crises.
These risks can pop up from anywhere:
- Market Volatility: Sudden shifts in the economy, exchange rates, or customer demand.
- Operational Hiccups: A vital piece of equipment breaking down or a key supplier going out of business.
- Financial Shocks: An unexpected interest rate hike or a major client defaulting on their payment.
The key to smart risk management is developing contingency plans. This means constantly asking "what if?" and creating a clear response ahead of time. What if our biggest client walks? What if our import costs suddenly double? Having a plan—like securing a line of credit or diversifying your customer base—means you can react calmly and decisively, instead of panicking when things go wrong. A truly robust financial plan doesn't just hope for the best; it prepares for the worst.
Building Your Financial Plan Step-by-Step
Putting together a business financial plan can feel overwhelming, but it’s less like climbing a mountain and more like assembling a piece of flat-pack furniture. If you follow the instructions and take it one step at a time, you can turn a confusing pile of numbers into a solid structure that genuinely supports your business. This framework breaks the whole process down into five manageable stages.
Think of it as tidying up a chaotic workshop. You're moving from a mess of tools and materials to a clean, organised space where you can actually build something.
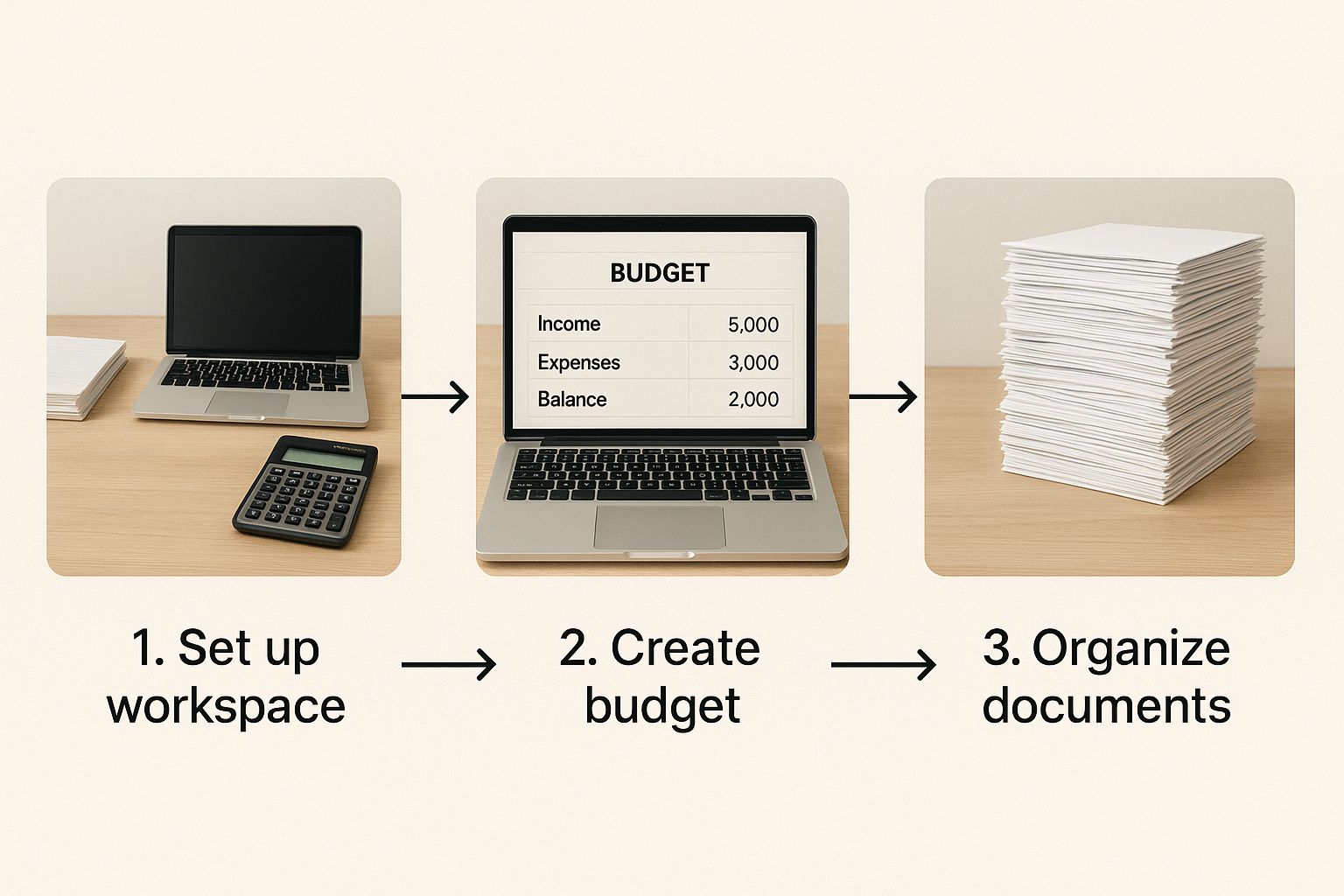
This image captures that journey perfectly—taking jumbled financial documents and transforming them into a clear, actionable plan on a laptop, which becomes the central hub for your strategic decisions.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Financial Health
Before you can map out a route to where you want to go, you need to know exactly where you're starting from. This first step is all about taking a completely honest look at your company’s current financial standing. It’s like getting a full health check-up for your business.
Pull together all your key financial documents to get the full picture. You'll need:
- Income Statements: These show you your revenue, costs, and profitability over a specific period.
- Balance Sheets: This gives you a snapshot of your assets, liabilities, and equity at a single point in time.
- Cash Flow Statements: This is crucial for tracking how money actually moves in and out of your business.
This isn’t about judging past performance; it’s about gaining clarity. This baseline analysis will highlight your financial strengths, like healthy profit margins, and expose any weaknesses that need attention, such as high debt levels or unpredictable cash flow.
Step 2: Set SMART Financial Goals
Once you have a clear picture of your current situation, you can start setting meaningful goals for the future. Vague ambitions like “make more money” simply won’t cut it. For a plan to work, your objectives need to be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
This framework turns wishy-washy ideas into concrete targets. For instance, instead of a goal to "grow the business," a SMART goal sounds like this: "Increase our export revenue by 15% within the next 12 months by expanding into two new regional markets."
Setting SMART goals gives your financial plan a clear sense of direction. Every decision that follows, from budgeting to forecasting, should directly support these specific, well-defined targets.
Step 3: Create Detailed Financial Projections
This is where you shift your focus from the present to the future. Using your historical data from Step 1 and the goals you set in Step 2, you'll build out detailed financial projections. These aren't just wild guesses; they are educated estimates based on real information.
Your projections need to cover a few key areas:
- Sales Forecast: Project how much revenue you expect to bring in. Factor in things like market trends, seasonal highs and lows, and any marketing campaigns you have planned. It's a good idea to create three versions: conservative, optimistic, and most likely.
- Expense Budget: List every single anticipated cost, from fixed expenses like rent and salaries to variable ones like raw materials and shipping. Always err on the side of caution and slightly overestimate your expenses to create a safety net.
- Cash Flow Projection: Map out the expected flow of cash on a monthly or quarterly basis. This is absolutely critical for spotting potential cash shortages before they become a crisis.
Step 4: Develop Contingency Scenarios
Let's be realistic—no business operates in a bubble. Things go wrong. Things go unexpectedly right. A truly resilient financial plan anticipates this uncertainty by building in contingency scenarios. It’s all about asking "what if?" and planning your response ahead of time.
Try to map out three main possibilities:
- Best-Case: What happens if your new product is a runaway success? How would you reinvest those extra profits to fuel more growth?
- Worst-Case: What if a major client goes bust or new import tariffs suddenly hit your bottom line? What costs could you cut immediately to stay afloat?
- Most-Likely: This is your baseline plan—the path you reasonably expect your business to take.
Thinking through these scenarios means you won't be caught flat-footed. It gives you the agility to pivot, whether you're seizing a surprise opportunity or navigating a sudden storm.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor the Plan
A financial plan gathering dust in a folder is worthless. It needs to be a living, breathing document that informs your day-to-day decisions. Implementation is about putting your budgets into action, while monitoring means regularly checking your actual results against what you projected.
Set a schedule for monthly or quarterly reviews to track your progress against your KPIs. Are you hitting your revenue targets? Are your expenses staying within the budget? This constant feedback loop is what allows you to make smart adjustments, celebrate what’s working, and correct your course when needed. It’s how you keep your business on a steady path to financial success.
Tracking the Metrics That Actually Matter
A financial plan is useless if you can't tell whether it's working. Think of it like a car's dashboard: it gives you critical feedback on speed, fuel, and engine health. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) do the same for your company's finances, providing the real-time data you need to know if you're on course or heading for trouble.
Just looking at your total revenue is a rookie mistake. Sure, it tells you money is coming in, but it reveals nothing about how efficiently you're running the show, how much you're actually keeping, or if you have enough cash to cover next month's payroll. A solid financial plan means digging deeper into the metrics that paint a true picture of your business's health.
Gauging Profitability and Efficiency
The first set of gauges on your financial dashboard should measure how well your business turns revenue into actual profit. These metrics go beyond the headline sales number to show you what’s really happening under the bonnet.
- Gross Profit Margin: This tells you how much profit you make on your core offering—your products or services—before factoring in general business overheads. A healthy margin here shows your pricing strategy and production costs are in a good place.
- Formula: (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
- Net Profit Margin: This is the real bottom line. It shows what percentage of revenue is left after every single expense, from rent and salaries to taxes and interest, has been paid. A low net margin is a classic sign that your operating costs are eating away at your success.
- Formula: Net Income / Revenue
These two margins are a powerful duo. If you have a high gross margin but a low net margin, it’s a massive clue that while your core business is strong, your administrative or marketing spend is probably out of control. This kind of insight allows you to make targeted fixes instead of just guessing where the money is going.
Think of it this way: Gross Profit Margin is the power your engine produces, while Net Profit Margin is the speed you actually achieve on the road. The difference between them is the friction—the operational drag you need to minimise.
Measuring Financial Stability and Risk
Profitability is great, but your dashboard also needs to measure stability. These KPIs are your early warning system, helping you spot potential cash flow crunches or dangerously high debt levels long before they become a full-blown crisis.
A key part of business financial planning is building resilience to handle unexpected bumps in the road. For South African businesses, especially those dealing with fluctuating exchange rates on international payments, tracking these stability metrics is non-negotiable.
Current Ratio (Liquidity) This KPI measures your ability to cover your immediate bills with assets you can quickly turn into cash. In plain English, can you pay everything you owe over the next 12 months using the resources you have on hand?
A ratio below 1.0 can be a major red flag for lenders and investors, suggesting you might struggle to pay your debts. A healthy ratio is typically between 1.5 and 2.0, indicating you have a comfortable buffer.
- Formula: Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Debt-to-Equity Ratio (Leverage) This ratio reveals how much of your business is financed by debt compared to how much is funded by your own capital (equity). It’s a direct measure of your financial risk.
A high ratio means you're heavily reliant on borrowing, which can become a problem if interest rates climb or your revenue takes a hit. While taking on some debt is often necessary for growth, a very high ratio can make it tough to secure more funding. Keeping an eye on this helps you strike a healthy balance between ambition and stability.
- Formula: Total Liabilities / Shareholder Equity
By consistently monitoring these four KPIs, your financial planning transforms from a static document into a dynamic process. You're no longer just following a map; you're actively driving, using your dashboard to make smart, proactive adjustments that keep you firmly on the road to sustainable success.
Overcoming Common Financial Planning Hurdles
Embarking on business financial planning is a brilliant move, but let's be honest—the path isn't always smooth. Every business, from a brand-new startup to a well-established enterprise, hits a few roadblocks. Knowing what these hurdles look like ahead of time is the first step to navigating them, ensuring your financial plan becomes a genuinely useful guide, not just a source of frustration.
Many business owners, especially when they're starting out, fall into the trap of inaccurate forecasting. It often comes from a good place—optimism! You project best-case scenarios for sales while, perhaps, underestimating what it really costs to keep the lights on. The result? A plan built on shaky ground, which can lead to serious cash flow shortages when reality doesn't quite match those rosy predictions.
Then there's the classic mistake of poor cash flow management. It's so easy to confuse profit on a spreadsheet with actual rands in the bank. You could have a record-breaking sales month, but if your clients pay on 60 or 90-day terms, you might still find yourself unable to cover salaries and supplier invoices next week.
The Pitfall of a "Set-and-Forget" Plan
One of the biggest—and most subtle—hurdles is treating the financial plan as a static, one-and-done document. A plan you create in January and never look at again is obsolete by March. Markets shift, new competitors pop up, and unexpected opportunities (or crises) land on your doorstep. A plan that doesn't adapt to these changes is as useless as an old map.
To avoid this, your financial planning has to be dynamic. Schedule regular check-ins—at least monthly for your cash flow and quarterly for the bigger picture strategy. This turns your plan into a living document that evolves with your business, allowing you to make proactive adjustments instead of putting out fires. Think of it as regularly recalibrating your ship's compass to account for changing currents.
A financial plan should be a verb, not a noun. It is an ongoing process of analysis, adjustment, and action that guides your business through the complexities of the real world. Neglecting it is like setting a destination and then refusing to touch the steering wheel.
Nuances for South African Businesses
Here in South Africa, businesses face a unique set of challenges that demand special attention in financial planning. This is particularly true for family-owned enterprises, which are a massive cornerstone of our local economy. These businesses often walk a tightrope, balancing ambitious growth goals with the deeply personal need to preserve a family legacy and ensure a smooth succession down the line.
This dual focus requires a more nuanced approach to things like risk management and deciding where to invest capital. Furthermore, digital transformation isn't just a buzzword anymore; it's crucial for survival and staying competitive. For many family businesses, adopting modern tools is key to boosting efficiency, but it often requires external financing to make that transition happen. This really highlights how these businesses must carefully weave operational upgrades into their long-term financial strategy. You can read the full KPMG report on family business perspectives.pdf) to get a deeper understanding of these trends.
Practical Solutions for Common Hurdles
Getting over these obstacles doesn’t require a complete overhaul. It's more about a shift in mindset and adopting some practical strategies. Here’s how you can tackle these common issues head-on:
- Build Conservative Forecasts: When you're projecting your numbers, always create three scenarios: best-case, worst-case, and most-likely. Then, base your operational budget on the most-likely or even the worst-case scenario. This builds a financial buffer that can save you from unexpected shortfalls.
- Prioritise Cash Flow Visibility: Use modern accounting software to get a real-time view of your cash position. Focus relentlessly on shortening your accounts receivable cycle (getting paid faster) while strategically managing your accounts payable (paying your own bills).
- Schedule Regular Reviews: Put monthly and quarterly financial review meetings in the calendar and treat them as non-negotiable. Use these sessions to compare your actual performance against your plan and make the necessary adjustments.
- Embrace Digital Tools: Manual spreadsheets are prone to human error and can’t give you real-time insights. Investing in good accounting and payment platforms improves accuracy and frees you up to focus on strategy instead of getting bogged down in data entry.
By anticipating these common pitfalls and putting practical solutions in place, you can transform your business's financial planning from a daunting chore into one of your most powerful strategic assets.
Using Modern Tools for Smarter Financial Management
Trying to manage your business's finances with manual spreadsheets is like using a paper map in the age of GPS. Sure, you might get there eventually, but it’s slow, full of potential wrong turns, and leaves you far behind the competition. Technology has completely changed the game, giving small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) access to powerful tools that were once reserved for huge corporations.
Bringing modern financial software into your business isn't just a nice-to-have; it's essential for building a resilient, competitive operation. These tools handle the tedious, repetitive tasks, deliver up-to-the-minute insights, and make your financial data incredibly accurate. This frees you up to think about the big picture, instead of getting buried in calculations.
Key Tool Categories for Your Business
To build a solid tech stack for your finances, you’ll want a few key types of software that play well together. Each one tackles a different piece of the financial planning puzzle.
- Accounting Software: This is your foundation, the central hub for your finances. Platforms like Xero and Sage automate everything from bank reconciliations to invoicing and payroll, giving you a live, accurate picture of your financial health.
- Budgeting and Forecasting Platforms: While your accounting software likely has some basic budgeting functions, dedicated forecasting tools are a massive step up. They analyse your historical data and market trends to build detailed financial models, helping you plan for different scenarios and project future cash flow with much greater confidence.
- Payment and Cash Flow Solutions: Getting money in and out of the business, especially across borders, can be a major headache. Modern payment solutions are built to make this process smooth, fast, and cheap, preventing delays and high fees from eating into your liquidity.
These tools don’t just speed up your old processes—they unlock a whole new, proactive way to manage your money. You shift from simply reacting to past events to making strategic decisions based on live data and reliable forecasts.
How Technology Empowers South African SMEs
In South Africa, SMEs are the lifeblood of the economy, making sharp financial management a top priority. Government initiatives are focused on equipping SME owners with the financial skills to handle challenges like market volatility and inflation. You can read more about these efforts in the SEDFA Annual Performance Plan for 2025-26_010425.pdf). Technology is a huge part of this, giving businesses everywhere access to world-class financial tools.
Think about an export business in Cape Town. In the past, they’d have to put up with slow, expensive international payments through traditional banks. Now, a platform like Zaro can slash transfer times and get rid of hidden forex markups, putting more cash directly back into the business. This isn't a small tweak; it's a real strategic advantage that makes the entire business financially stronger.
Integrating Tools for Maximum Impact
The real magic happens when you connect these systems. When your payment platform automatically sends transaction data to your accounting software, which in turn syncs with your forecasting tool, you create a seamless flow of information. This gets rid of manual data entry, cuts down on human error, and gives you one reliable source of truth for all your financial decisions.
Picture this workflow:
- An international client pays your invoice. The money arrives quickly through a modern payment solution like Zaro, at a fair and transparent exchange rate.
- The transaction is automatically recorded and categorised in your Xero or Sage account. No manual input needed.
- Your cash flow forecast instantly updates with the new balance, giving you a precise, real-time view of your available cash.
This kind of automation turns business financial planning from a stressful, periodic chore into a continuous, manageable process. It lets you stay agile, act strategically, and truly be in control of your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Getting started with financial planning often brings up a few common questions. Let's tackle some of the most frequent ones so you can move forward with confidence.
How Often Should I Review My Business Financial Plan?
Think of your financial plan as a living document, not something you create once a year and file away. While the big, comprehensive plan is usually mapped out annually, your real-world progress needs more frequent attention.
At a minimum, you should be checking in on your budget and cash flow forecasts every month. This helps you spot small issues before they become big problems. Then, every quarter, set aside time for a deeper dive. This quarterly review is your chance to react to market shifts, see how you’re tracking against your bigger goals, and adjust for anything unexpected that’s come up.
What Is The Biggest Mistake Startups Make In Financial Planning?
The classic, and most dangerous, mistake is a double-whammy: overestimating how much you'll sell and underestimating how much things will cost. This "optimism gap" can drain your cash reserves with alarming speed. It's no surprise that studies link 82% of business failures to poor cash management.
The antidote is realism. Ground your sales forecasts in solid market research, not just hope. On the expense side, be brutally honest and list everything you can think of. Then, add a contingency fund of at least 15-20% on top of that for the inevitable surprises. It's always better to be pleasantly surprised by extra cash than caught short.
Can I Do My Own Financial Planning Or Do I Need A Professional?
You can absolutely handle the day-to-day basics yourself, and frankly, you should. As a business owner, having a firm grip on your numbers is non-negotiable, and modern software makes this more manageable than ever.
However, bringing in a professional financial advisor or accountant, especially at key moments, is a smart investment. They are invaluable when building your first comprehensive plan, navigating the complexities of tax, or making major strategic decisions. Their expert, impartial eye can help you sidestep costly errors and spot opportunities you might have overlooked, making sure your business is built on a rock-solid financial foundation.
Take control of your global payments and strengthen your financial planning. With Zaro, you get the real exchange rate with zero hidden fees, giving you the clarity and efficiency needed to manage your cash flow effectively. Discover how much you can save.
