Understanding Your Real FX Exposure in the SA Market

Doing business in South Africa, especially if you're importing or exporting, means dealing with the unpredictable rand. Every South African business knows that foreign exchange (FX) risk exposure can significantly impact their profits. But many underestimate the true extent of this risk. It goes beyond the obvious fluctuations in exchange rates. It's about recognizing the hidden ways currency volatility affects your bottom line.
Even small payments to overseas suppliers can become surprisingly costly when the rand weakens. Successful companies dig deeper than traditional accounting methods to uncover these hidden exposures. They adopt proactive foreign exchange risk management, a critical strategy in today's interconnected global economy.
Identifying Your FX Exposures
Effective foreign exchange risk management starts with understanding the different types of currency exposure your business faces. There are three main categories to consider:
Transaction Risk: This risk arises from exchange rate fluctuations affecting future payments or receipts. For example, if you agree to pay a supplier in US dollars in three months, and the rand weakens against the dollar during that time, you'll end up paying more in rand than you initially budgeted.
Translation Risk: This risk emerges when consolidating financial statements that include assets and liabilities held in foreign currencies. If you own assets denominated in a foreign currency that depreciates against the rand, the rand value of those assets will decrease on your balance sheet.
Economic Risk: This is the most complex type of FX risk. It reflects the long-term impact of currency movements on a company's market value and competitiveness. A weaker rand can make your exports cheaper, but it can also increase the cost of imported materials, affecting your profit margins. Analyzing long-term cash flow projections is key to understanding this risk.
By understanding these different exposures, you can develop targeted risk management strategies. A 2013 survey showed just how significant currency risk is for South African businesses. 67% of companies ranked it as a top-three risk, with 91% reporting sensitivity to exchange rate movements. Find more detailed statistics here. This highlights the vital role of proactive foreign exchange risk management in the South African market.
Why a Proactive Approach is Essential
Global events, fluctuating commodity prices, and even local political changes can all increase currency risks for South African businesses. Consider the effect of global commodity prices on the rand, particularly given South Africa's dependence on resource exports. Falling commodity prices can weaken the rand, impacting businesses that import goods or services.
Shifts in global risk sentiment can trigger capital flight from emerging markets like South Africa, further pressuring the rand. Domestic political uncertainty also plays a role in currency volatility. Because of these interconnected factors, a proactive approach is essential. Instead of simply reacting to currency fluctuations, businesses need to implement strategic measures to mitigate potential risks. This proactive approach can significantly impact profitability and long-term financial stability.
Measuring FX Risk Like the Pros Do It

Accurately measuring foreign exchange (FX) risk is fundamental to effective management. Simply acknowledging the volatility of a currency like the South African rand isn't enough. You need to quantify your exposure. Leading JSE-listed companies understand this, using sophisticated, practical techniques to measure their currency risk. This moves them beyond guesswork and into data-driven strategies.
Value-at-Risk (VaR): Understanding Potential Losses
One common method is Value-at-Risk (VaR). VaR calculates the potential loss in a portfolio's value over a specific time and confidence level. For example, a VaR of R1 million at a 95% confidence level over one week means there's a 5% chance of losing R1 million or more within that week. This helps businesses understand the potential downside of FX exposure.
Scenario Analysis: Preparing for Different Possibilities
While VaR offers a statistical snapshot, scenario analysis explores the potential impact of specific events on your business. These could include a sudden drop in commodity prices or a shift in global investor sentiment. By modeling these "what-if" scenarios, companies can proactively identify vulnerabilities and develop appropriate responses, preparing for various market conditions.
Stress Testing: Evaluating Resilience Under Extreme Conditions
Similar to scenario analysis, stress testing assesses your company's resilience under extreme, yet plausible, scenarios. These often involve more severe market fluctuations than typical scenario analysis. For example, stress testing might model a major currency crisis or a significant political event. This helps uncover hidden weaknesses and ensures your FX risk management strategies can withstand serious pressure.
A study highlighted the substantial FX exposure of JSE-listed non-financial firms. Their exposure to major currencies like the US dollar (34.4%), British Pound (33.3%), and Euro (37.8%) underscores the need for robust risk management. Explore this topic further. These figures help companies understand their positions relative to these currencies.
Econometric Approaches: Delving Deeper Into Data
Econometric models can provide a deeper understanding of the relationship between exchange rate movements and specific business variables. While potentially complex, these approaches offer valuable insights for managing FX risk. Analyzing historical data helps identify patterns and predict future exchange rate behavior more accurately, leading to more strategic hedging decisions.
Industry Benchmarks and Ongoing Monitoring: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Comparing your FX exposure to industry benchmarks provides valuable context, showing how your risk profile compares to similar companies in the South African market. Furthermore, a framework for ongoing monitoring allows for dynamic adjustments, crucial in the ever-changing FX market. Regularly reviewing your measurements and hedging strategies allows you to adapt to new market conditions and maintain an effective risk management approach.
Building Hedging Strategies That Actually Work
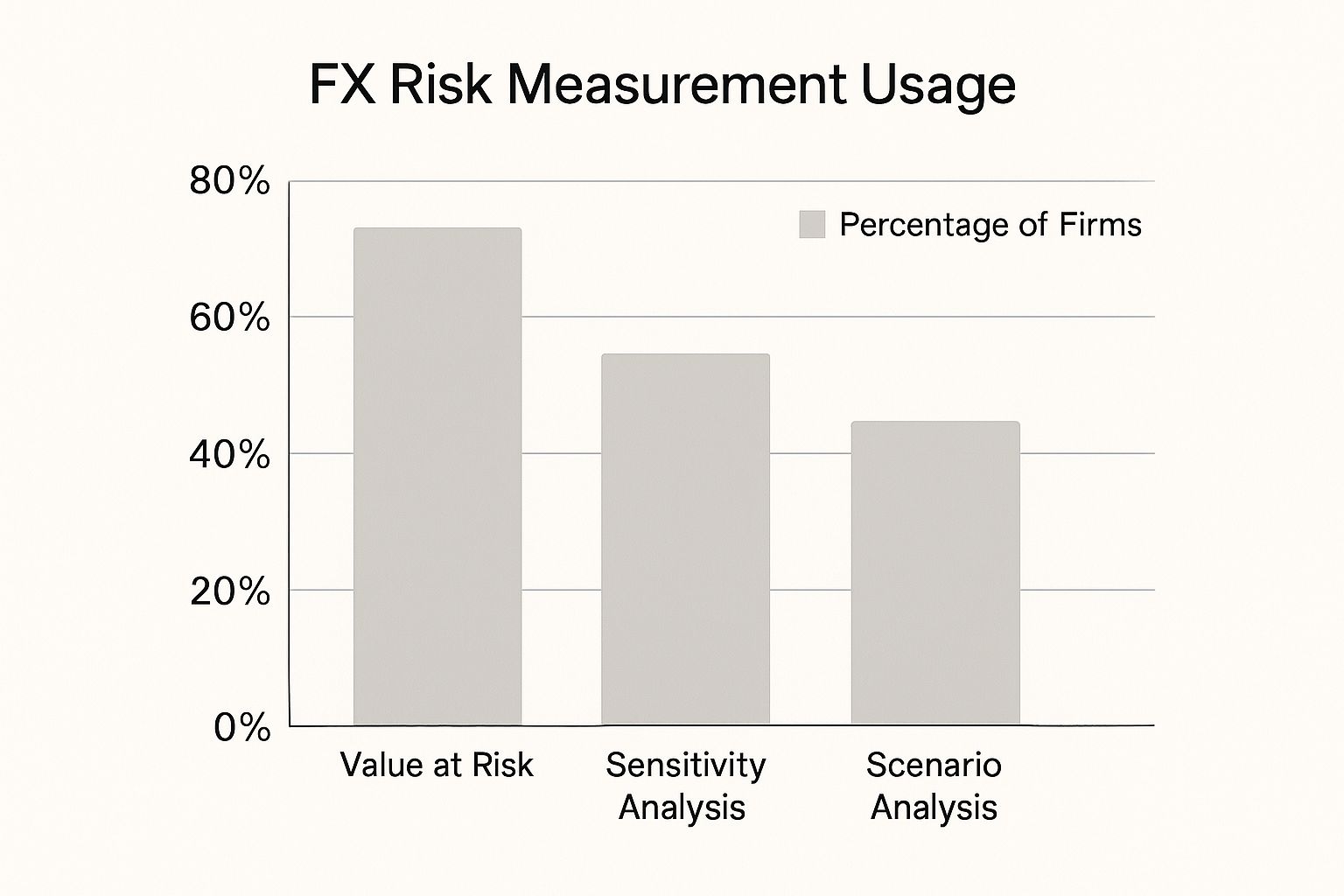
The chart above visualizes how South African businesses adopt various FX risk measurement methods. It shows how common techniques like Value at Risk, Sensitivity Analysis, and Scenario Analysis are. Value at Risk is the most frequently used method. However, a significant number of companies also use sensitivity and scenario analyses, demonstrating a multifaceted approach to FX risk assessment in South Africa. This suggests a proactive effort to understand and measure currency risks. Let's explore how these measurements inform practical hedging strategies.
Practical Hedging for the South African Market
Successfully managing the rand's volatility requires more than theoretical knowledge. It requires practical hedging strategies designed for the specific challenges and opportunities South African businesses face. Savvy South African businesses focus on balancing cost and protection. This means understanding the costs of different hedging tools and how they impact profitability.
To help illustrate the practical application of these tools, let's examine a comparison of their costs, protection levels, complexity, and suitability for different SA business scenarios:
To provide a clearer picture of how these tools compare, we've compiled the following table:
SA Company FX Hedging Tools: Real-World Comparison
| Hedging Tool | Typical Cost | Protection Level | Complexity | Best For SA Companies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Contracts | Low | Fixed | Simple | Businesses needing predictable exchange rates for specific transactions, like importing or exporting goods. |
| Currency Options | Medium | Customizable (upside potential or downside protection) | Moderate | Businesses wanting flexibility to benefit from favorable rate moves while limiting downside risk. Ideal for uncertain market conditions. |
| Currency Swaps | High | Ongoing, long-term | Complex | Businesses managing long-term currency exposures, often related to debt or ongoing international operations. |
This table provides a concise overview of how different hedging tools can be applied. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific needs and risk tolerance of each business.
Structuring Your Hedging Approach
Effective hedging goes beyond individual transactions. Developing a comprehensive hedging policy is crucial. This includes defining the percentage of anticipated foreign currency transactions to hedge. Some companies use a tiered approach. For example, they might hedge 80% of short-term exposures, 50% of medium-term exposures, and 25% of longer-term exposures. This reflects the growing uncertainty of future cash flows.
Timing is also critical. Deciding when to execute hedges requires careful consideration of market conditions, risk appetite, and business forecasts. Businesses can benefit from establishing trigger mechanisms that automatically initiate hedges when pre-defined exchange rate thresholds are breached. This removes emotional decision-making during market volatility.
The Importance of FX Risk Committees
Many South African companies establish FX risk committees with representatives from treasury, finance, and relevant business units. These committees play a vital role in setting risk limits, approving hedging strategies, and monitoring performance. Regular reporting to senior management and the board of directors ensures accountability and aligns FX risk management with overall business objectives. This integration into broader financial planning ensures hedging decisions don't have unintended consequences elsewhere. Recognizing the dynamic FX market, these committees regularly review policies and strategies. This ensures they're up-to-date and effectively mitigate evolving risks.
Mastering Rand Trading Patterns and Market Dynamics

Understanding the dynamics of rand trading is crucial for effective foreign exchange risk management. This goes beyond simply knowing the current exchange rate. It requires a deeper understanding of the factors influencing its movements, from global market sentiment to local South African economic indicators. This knowledge can significantly reduce hedging costs and optimize currency strategies.
Decoding the Drivers of Rand Fluctuations
Several structural factors contribute to the volatility of the South African rand. A major influence is commodity correlations. South Africa has a resource-driven economy, making its currency highly sensitive to fluctuations in commodity prices. A decline in gold or platinum prices, for example, can quickly weaken the rand.
Global risk sentiment also plays a vital role. Emerging market currencies, like the rand, are particularly susceptible to shifts in global sentiment. They often experience significant outflows during periods of global uncertainty, highlighting the interconnectedness of global finance and its impact on local currencies.
Understanding these relationships is paramount for accurately assessing and managing foreign exchange risk, especially when considering the rand's historical trading patterns. Turnover statistics provide key insights into this dynamic.
For example, the vast majority (95%) of rand transactions occur against the US dollar, underscoring its dominance. While daily turnover peaked at US$20.0 billion in 2016, it decreased to US$13.8 billion by July 2019. Discover more insights about rand trading volumes. This shift highlights the importance of monitoring trading patterns for effective risk management.
Identifying Optimal Hedging Timing
Reading market signals is crucial for optimizing hedging timing. Certain periods offer more favorable execution opportunities. Specific times of day, week, or even month can exhibit increased liquidity, leading to better exchange rates. These patterns stem from various factors, including market activity in different time zones and the release of significant economic data.
Local economic releases, such as inflation data or interest rate decisions by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB), can create substantial volatility. Political developments, both domestic and international, can also impact the rand. Careful monitoring of these factors allows businesses to identify optimal times to execute hedges, potentially leading to cost savings.
Managing Dealing Costs and Market Impact
Liquidity patterns directly influence dealing costs in the foreign exchange (FX) market. Understanding these patterns can result in substantial savings. Trading during periods of high liquidity typically results in lower transaction costs.
Implementing appropriate execution strategies, such as breaking up large trades into smaller ones, can minimize market impact. This is particularly important for businesses with significant foreign currency transactions.
Building Relationships With FX Dealers
Developing strong relationships with FX dealers is essential for effective foreign exchange risk management. Dealers who understand your business needs can provide valuable insights and assist in developing tailored hedging strategies. These relationships offer personalized support and guidance, helping navigate the complexities of the FX market. This personalized service is crucial in a volatile market like South Africa's.
Creating FX Risk Frameworks That Stand the Test
Successfully managing foreign exchange risk means moving past reactive decisions. A strong FX risk framework provides the systematic processes needed to navigate volatile markets, especially concerning the often-fluctuating South African rand. This section explores how well-established companies structure their FX risk governance, from board oversight to day-to-day activities.
Establishing a Solid Foundation: Risk Policies and Governance
A clearly defined risk policy offers necessary guidance without being overly rigid. It should outline the company’s risk appetite, accepted hedging instruments, and reporting requirements. This structure allows for flexibility while ensuring responsible actions are taken. It establishes boundaries, not barriers.
Good governance begins at the highest level. Board-level oversight guarantees FX risk management aligns with the overall business strategy. This includes establishing clear responsibilities from the board to treasury operations.
Practical Approaches to Risk Committees
Risk committees, composed of members from treasury, finance, and related departments, are key to applying the risk policy. They make important decisions on hedging strategies, determine appropriate risk limits, and constantly monitor FX exposure. This teamwork ensures decisions are informed and support the company’s financial objectives.
Effective delegation of authority is vital. The risk committee should have the power to approve hedging transactions within set limits. Larger, more complex transactions might need board approval. This multi-level approach streamlines decisions while maintaining proper control.
To understand how companies of different sizes approach FX risk management, let's examine the following comparison:
FX Risk Management by Company Size: What Really Works
Realistic breakdown showing how small, medium, and large SA companies structure their FX risk management based on actual resources and business complexity
| Company Size | Governance Structure | Hedging Tools | Reporting Needs | Resource Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Basic risk policy, often managed by the CFO | Forward contracts, natural hedging | Simple reports focused on key exposures | Limited internal resources, may rely on external advisors |
| Medium | Dedicated treasury function, formal risk committee | Options, FX swaps, in addition to forwards | Detailed reports on hedging activity and effectiveness | Moderate internal team, possibly supplemented by specialized software like Treasury Management Systems |
| Large | Sophisticated risk management department, board-level risk committee | Complex hedging strategies, potentially using specialized derivatives | Comprehensive reports covering all aspects of FX risk, often integrated with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems | Large, dedicated team with advanced analytical capabilities and access to sophisticated tools. |
Key takeaways from the table: smaller companies rely on simpler tools and structures, while larger businesses have dedicated teams and more complex strategies. Resource allocation reflects the complexity of the company's operations.
Reporting and Performance Measurement
Reporting should be clear, concise, and focused on important metrics. Stakeholders need relevant information presented effectively. Reports should highlight key exposures, hedging activities, and how well the risk management strategy is working. This allows for quick responses and strategic changes.
Performance measurement should focus on minimizing the negative effects of FX on profits. This might involve tracking hedging costs, the effectiveness of hedging in reducing volatility, and FX’s impact on profit margins. These concrete measurements demonstrate the value of FX risk management.
Maintaining a Dynamic Framework: Reviews and Crisis Management
Regular reviews are essential. The risk policy, hedging strategies, and even the members of the risk committee should be reviewed periodically. This ensures the framework adapts to the business environment.
A solid crisis management plan is also crucial. This outlines steps for extreme market events, like a major currency crisis. It should include communication protocols, backup funding, and clear decision-making authority in emergencies. This allows for quick, decisive action to limit losses.
Technology Tools That Make FX Management Easier
Modern technology is reshaping how South African businesses manage foreign exchange (FX) risk. With a multitude of options available, understanding which tools are worth the investment is crucial. This section explores the technology driving this change, focusing on solutions suitable for South African businesses.
Treasury Management Systems: Automating the Essentials
Treasury Management Systems (TMS) automate routine tasks, allowing your finance team to focus on strategic initiatives. These systems centralize FX exposure data, automate hedging transactions, and integrate with other financial platforms like SAP or Oracle. This reduces manual errors and provides real-time visibility into your currency risk.
Key features of a TMS include:
- Real-Time Exposure Monitoring: Track FX positions across various currencies and entities.
- Automated Hedging Triggers: Execute hedges automatically based on pre-defined parameters.
- Integrated Reporting: Generate comprehensive FX risk reports, eliminating hours of manual effort.
These benefits make TMS a critical component for effective FX risk management in a dynamic currency market like South Africa's.
Risk Analytics Platforms: Enhancing Decision-Making
Risk analytics platforms offer advanced tools for analyzing and visualizing FX risk. They often include features like scenario analysis, stress testing, and econometric modeling. These capabilities enable businesses to make data-driven hedging decisions and gain a better understanding of potential losses under various market conditions.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Accessibility for All
Cloud-based FX management solutions provide even small South African businesses with access to sophisticated tools. These solutions often offer flexible pricing and scalability, allowing businesses to adapt as their needs evolve. This empowers smaller companies to manage currency risk effectively.
Choosing the Right Technology
Selecting the right technology depends on your company's size, complexity, and risk management maturity. Avoid overcomplicating your technology stack. A simple TMS might suffice for a small import/export business. A larger multinational corporation might benefit from a comprehensive risk analytics platform.
Consider the following factors when choosing an FX management solution:
- Implementation: How easily can the technology be integrated into your current systems?
- Data Integration: Can the system connect with your existing accounting and ERP software?
- User Training: Is the platform user-friendly and easy for your team to learn?
- Cost-Benefit: Does the potential improvement in FX risk management outweigh the cost of the technology?
Carefully evaluating these factors ensures you have the right tools for efficient FX risk management without unnecessary complexity.
Making Your FX Strategy Stick: Implementation That Works
A robust foreign exchange risk management strategy is only as good as its implementation. This section provides a roadmap for South African businesses to translate FX theory into practical, everyday actions, ensuring sustainable success in managing currency volatility.
Building Consensus and Fostering Internal Support
Successful implementation begins with buy-in. Getting everyone on board, from the executive team to front-line staff, is crucial for long-term success. This involves clearly communicating the benefits of foreign exchange risk management, not just for the company as a whole, but for individual departments and roles.
Training is another key element. Equipping your staff with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively execute the FX strategy empowers them to take ownership of their role in managing currency risk. Building internal champions who actively promote the program within their teams can help sustain momentum and ensure adherence to best practices.
Measuring Success and Driving Continuous Improvement
Establishing clear performance metrics demonstrates the value of your FX strategy. These metrics might include reduced hedging costs, improved forecast accuracy, or the overall impact on profit margins. Regularly tracking and reporting on these metrics shows stakeholders the tangible benefits of the program.
Regular strategy reviews are essential for ongoing improvement. These reviews should assess the effectiveness of current hedging strategies and identify areas for refinement. Market conditions change constantly, so your FX strategy must adapt. Flexibility and the ability to adjust to evolving market dynamics are key to long-term success.
Addressing Implementation Challenges
Implementation inevitably comes with challenges. Understanding these challenges and proactively finding solutions is crucial. One common hurdle is the complexity of hedge accounting. Having clear procedures and potentially leveraging technology can help simplify the process.
Regulatory compliance is another important consideration. Staying informed of the latest regulations and ensuring your FX strategy aligns with them is crucial to avoid potential penalties. This requires continuous vigilance and a proactive approach to compliance.
Communication and Maintaining Momentum
Effectively communicating your FX strategy to stakeholders is vital for maintaining support and confidence. Regular updates on performance and market conditions help stakeholders understand the reasoning behind decisions and build trust in the process.
Maintaining momentum through different market cycles can be difficult. When markets are calm, it's tempting to abandon systematic approaches. However, it's during these times that discipline is most important. Reinforcing the long-term benefits of FX risk management helps maintain focus and prevent complacency. This consistent application of the strategy, regardless of market conditions, is key to sustained success.
Ready to take control of your foreign exchange risk and optimize your international payments? Zaro offers South African businesses a faster, more cost-effective solution for cross-border transactions. Eliminate hidden fees and gain greater control over your FX exposure. Visit Zaro today to learn more.