Ever found yourself lost in a sea of currency jargon? You're not the only one. Put simply, forex is the giant global marketplace where currencies are traded, and it has a very real impact on your South African business every single time you pay an overseas supplier or send an invoice to a foreign client. Getting to grips with it is less about becoming a day trader and more about protecting your profits.
Why Forex Matters for Your Business

Picture the forex market as a massive, sprawling city square that never sleeps, open 24 hours a day, five days a week. But instead of trading fruit and veg, the stalls are dealing in currencies—swapping South African Rand for US Dollars, Euros for British Pounds, and every other combination imaginable. Every time your business deals with another country, you're stepping right into this marketplace.
And this isn't just a game for the big corporates. If you're running a small or medium-sized enterprise (SME) here in South Africa, you're already in the forex game, whether you know it or not.
Everyday Business Activities Involving Forex
Even the most straightforward transactions are exposed to the whims of currency movements. Think about these common scenarios for a South African business:
- Paying for international software: That monthly subscription for your CRM or design tool? It’s almost certainly priced in US Dollars.
- Importing goods or raw materials: When you buy stock from a supplier in China, you have to exchange your Rand for their Yuan to settle the bill.
- Invoicing overseas clients: You might bill a customer in America in Dollars, but you'll eventually need to convert that payment back into Rand.
In every one of these situations, the exchange rate on the day the money actually moves determines how much you really pay or receive in your own currency. This brings us to the heart of the problem for any business owner.
How Currency Fluctuations Impact Your Profit
The value of the South African Rand is constantly shifting against other currencies. This volatility is a silent profit killer.
Let’s say you agree to sell products to an American client for $5,000. On the day you raise the invoice, the exchange rate is a comfortable R19 to the Dollar. You're expecting to bank R95,000. But a month later, when the payment finally clears, the Rand has strengthened to R18/$. Your $5,000 is now only worth R90,000.
Just like that, you've lost R5,000. It wasn't a bad sale or a mistake on your part; it was a financial hit caused purely by currency risk.
This is the unpredictable nature of forex. It turns careful financial planning into a bit of a guessing game. A deal that looked profitable on paper can end up as a loss, and a budgeted cost can suddenly spiral. That's why understanding the forex basics isn't some abstract financial exercise—it's a vital skill for protecting your company's health and making sure your hard-earned profits stay where they belong: in your bank account.
How the Forex Market Actually Works
When you hear the word "market," you probably picture the Johannesburg Stock Exchange building. But the forex market is completely different. It has no physical address, no central headquarters. Instead, it’s a vast, decentralised digital network connecting banks, corporations, and financial institutions across every time zone.
This is what allows the market to run 24 hours a day, five days a week. It literally follows the sun around the globe, kicking off with the Sydney session, moving through Tokyo and London, and finally wrapping up when New York closes. Because of this, currency values are constantly shifting, reacting to economic news and global events as they happen.
The Major Players in the Forex Ecosystem
The forex market isn't just a chaotic free-for-all. It’s an ecosystem with several key players, and knowing who they are helps make sense of how currency prices are set and how money moves around.
- Central Banks: Think of institutions like the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) as the giants of the market. They aren’t trading to make a profit. Their goal is to manage the country's currency value, keep inflation in check, and stabilise the economy, often by adjusting interest rates or buying and selling foreign currencies.
- Commercial Banks: These are the market's main dealers. They handle the vast majority of transactions for their clients—everyone from huge multinational corporations to small businesses—and also trade on their own behalf.
- Corporations and SMEs: This is where your business fits in. Any company that imports goods, exports products, or deals with international clients is a participant. When your business needs to pay a supplier in US dollars or receive a payment in euros, you’re contributing to the market's massive daily volume.
It’s this constant push and pull between different players, all with their own objectives, that makes the forex market so liquid and dynamic.
South Africa's Role in the Global Market
It’s easy to think of forex as something that happens far away, but South Africa is a major player, especially on the continent. Our local market isn't just large; it's growing at an incredible pace.
South Africa's forex market is projected to grow from USD 3,861.60 million to USD 6,852.50 million by 2033. The country leads Africa with a daily turnover exceeding $20 billion, driven by advancements in electronic trading platforms championed by the SARB.
This enormous scale has a direct effect on your business. The cost of fuel for your delivery bakkies, the price of imported equipment, and even the interest rates on your business loans are all influenced by what happens in this global market. You can explore more insights into Africa's forex outlook from Contentworks Agency.
Because forex is an over-the-counter (OTC) market, transactions happen directly between two parties, usually through a network of dealers, rather than on a centralised exchange. This is what allows it to be so huge and accessible around the clock. But it also means that understanding the details—like hidden fees and exchange rate markups—is absolutely critical for protecting your bottom line. With this foundation, you're now ready to get to grips with the key terms that define every single forex transaction.
Decoding Key Forex Terms You Need to Know
Dipping your toes into the world of foreign exchange can feel like trying to learn a new language overnight. But here’s the good news: as a South African business owner, you don’t need to be fluent. You just need to grasp the essential phrases that directly affect your bottom line. Let's ditch the textbook definitions and translate this jargon into practical, everyday business sense.
The single most important concept to understand is that every forex transaction involves two prices, not one. There's a price to buy a currency and a slightly different price to sell it. This tiny gap is where a lot of the costs are hidden, and seeing it clearly is the first step toward protecting your hard-earned profits.
The Spot Rate: The Price for Right Now
The spot rate is simply the live, real-time exchange rate for a currency pair. Think of it as the price tag on an item in a shop—it’s what you would pay if you decided to exchange your Rands on the spot, right this second.
For instance, if you need to pay a US-based supplier today, the spot rate is the immediate conversion price for ZAR to USD. This rate is constantly on the move, fluctuating with every piece of economic news and shift in market mood. It's the baseline rate that all other fees and costs are built on top of.
The diagram below shows the key players whose actions create these constant shifts in the forex ecosystem.
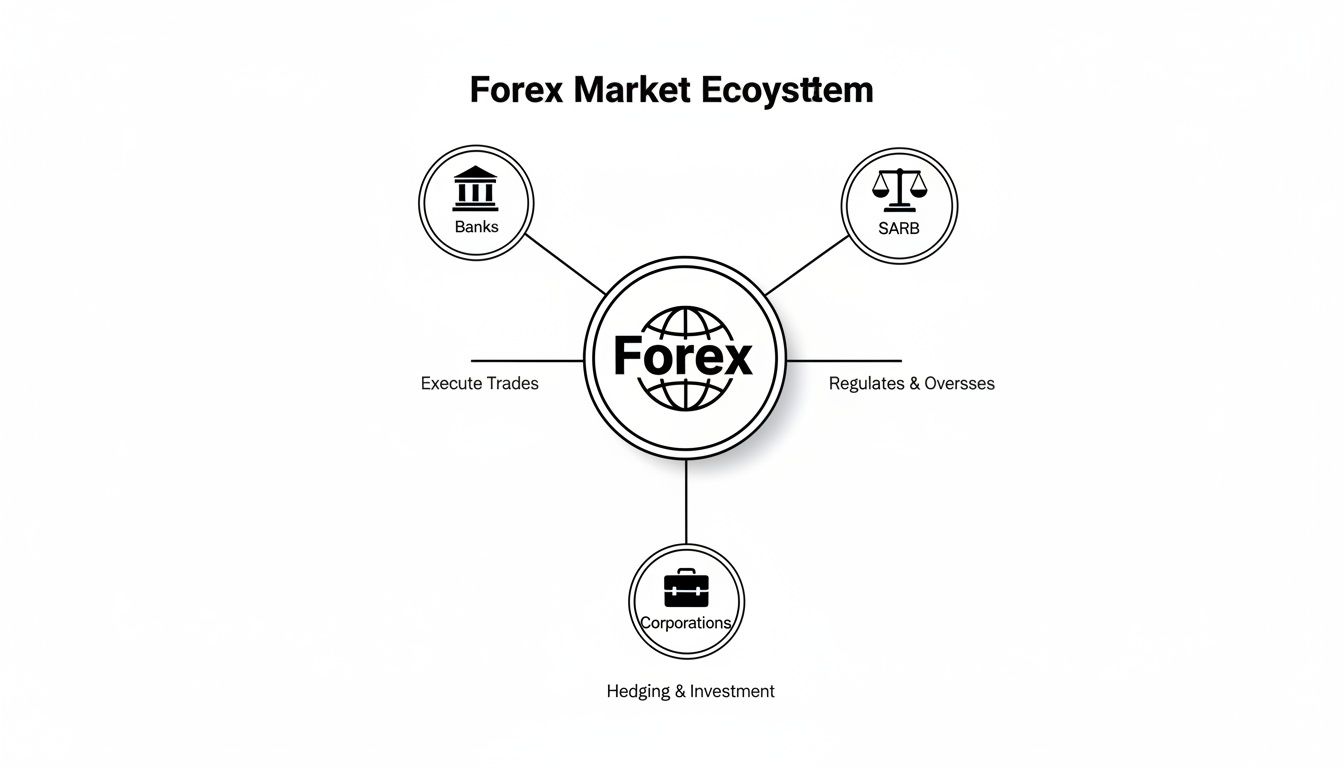
This map helps visualise how central banks like the South African Reserve Bank (SARB), commercial banks, and large corporations all interact, influencing the supply and demand that determines a currency's value.
The Spread: The Hidden Service Charge
Now we get to the most critical term for any business budget: the spread. In simple terms, the spread is the difference between the buy price (bid) and the sell price (ask) of a currency.
Here's a relatable analogy: you're buying tickets for a concert. The ticket has its face value, but the final price you pay includes a "service charge." The spread in forex works in exactly the same way. It’s the markup or fee that the bank or broker adds on top of the real spot rate.
The spread is pure profit for the financial institution handling your transaction. A wider spread means they are taking a bigger cut, and you are getting a worse deal.
This is precisely how many traditional banks make their money on international payments. They might advertise "zero commission," but they build their profit directly into an unfavourable exchange rate by making the spread as wide as they can.
Pips: The Smallest Step
A pip, which is short for "percentage in point," represents the smallest possible movement in an exchange rate. For most currency pairs, including the USD/ZAR, a pip is the fourth decimal place (0.0001).
Think of pips like cents to the Rand. While a single cent seems insignificant, they add up quickly. In the same way, a shift of just a few pips on a large business transaction can translate into a significant cost or saving. It's the unit we use to measure your profit or, more importantly, the cost of the spread you're paying.
Leverage: A Financial Magnifying Glass
Leverage is a tool that allows traders to control a large amount of currency with only a small amount of their own capital. It’s a bit like using a small deposit to secure a large bond on a property; you get to control the whole asset with just a fraction of its value.
However, for most South African SMEs involved in importing or exporting, leverage is more of a risk than a tool. It's designed for speculative trading, not for straightforward business payments. When you're paying suppliers or receiving money from overseas clients, your focus should be on locking in the best possible exchange rate, not amplifying your financial exposure with leverage.
This handy table breaks down these essential terms with simple analogies to help them stick.
Essential Forex Terms for Business Owners
| Term | Simple Explanation | Business Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Spot Rate | The immediate, live exchange rate for a currency pair. | The price of a coffee you buy right now at the counter. |
| Spread | The difference between the buy and sell price of a currency. | The "service fee" added to a concert ticket's face value. |
| Pip | The smallest unit of change in a currency's price. | The cents that make up a Rand; small on their own, but they add up. |
| Leverage | Using borrowed capital to increase potential returns (and risks). | A bond on a house; you control a large asset with a small deposit. |
By mastering this basic vocabulary, you stop being a passive participant and become an informed business owner. You can now read a currency quote with confidence, question the spread you’re being offered, and start spotting exactly where you might be losing money on your international transactions.
How Currency Volatility Threatens Your Bottom Line
Predictable revenue is the lifeblood of any business. It’s what lets you plan for the future, invest in growth, and meet your monthly obligations with confidence. But if you’re doing business across borders, currency volatility is a constant, invisible threat to that stability. It can turn a great month into a losing one, all without you changing a single thing about how you operate.
This isn’t about some high-level financial wizardry. It’s about the very real impact a fluctuating South African Rand has on your bottom line. One day, the Rands you expect from your export earnings look healthy; the next, a shift in the market has quietly erased thousands from your profit margin.
What Makes the Rand So Unpredictable?
The Rand doesn't move in a vacuum. Its value is constantly being pushed and pulled by a powerful mix of local and global forces. Getting a handle on these drivers is the first step towards protecting your business from the turbulence they create.
A few key factors are always in play:
- Local Interest Rates: When the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) makes an announcement, the world listens. Their decisions can either attract foreign investment, strengthening the Rand, or send it in the other direction.
- US Economic News: The US Dollar is the world’s main reserve currency, so news from the US Federal Reserve on interest rates or employment data sends ripples across the entire globe, directly hitting the USD/ZAR exchange rate.
- Commodity Prices: South Africa is a major exporter of resources like gold and platinum. As a result, our currency’s fate is often tied to the global prices of these commodities. A dip in the gold price, for instance, can quickly weaken the Rand.
- Geopolitical Events: Global uncertainty makes investors nervous. When that happens, they often rush to the perceived safety of currencies like the US Dollar, which can cause the Rand to drop.
The ZAR’s well-known volatility makes managing foreign exchange risk a non-negotiable for any South African business with international dealings. This is especially true when economic signs are mixed, like dipping foreign exchange reserves and a shrinking manufacturing sector. These situations are often made worse by global events, like policy shifts from the Fed or meetings of the European Central Bank, which can trigger huge market swings. For more on this, you can get insights on the Rand's turbulent outlook from Sable International.
A Real-World Example of Volatility Risk
Let's put the theory aside and look at a situation you might find yourself in. Imagine you run a software development company in Cape Town and you’ve just wrapped up a big project for a client in the United States.
You send them an invoice for $10,000. On that day, the exchange rate is R19 to the US Dollar.
Expected Revenue: $10,000 x 19.00 = R190,000
You plug that number into your cash flow forecast, feeling pretty good. But your client has 30-day payment terms. Over the next month, the market moves against you. By the time the money actually lands in your account, the Rand has strengthened to R18/$.
Actual Revenue: $10,000 x 18.00 = R180,000
Just like that, your business is R10,000 short. That loss had nothing to do with your service, a discount you offered, or any decision you made. It was caused entirely by currency market volatility—a risk you were exposed to without even realising it.
Hedging Is Just Good Business Insurance
This is exactly where hedging comes into the picture. Don't let the word intimidate you. It isn't some complex trading scheme; it's simply a form of financial insurance. In the same way you insure your office against fire, you can hedge against negative currency movements to protect your income.
By using a financial tool like a forward contract, you can lock in today's exchange rate for a payment you’ll receive in the future. In our example, you could have locked in the R19/$ rate on day one. That would have guaranteed you received the full R190,000, no matter what the market did over the next 30 days.
This simple strategy takes a huge unknown and turns it into a certainty. To dive deeper into safeguarding your business, understanding the various methods for managing foreign exchange risk is crucial. Ultimately, it’s about taking back control over your international finances, making your revenue predictable, and shielding your hard-earned profits from the chaos of the market.
A Better Way to Handle Your Business Forex
After seeing how currency volatility can quietly eat into your profits, it’s pretty clear that the old way of handling international payments just doesn’t cut it anymore. For years, South African businesses have had little choice but to use traditional banks for their forex needs. That meant accepting murky fees and sluggish processing times as just another cost of doing business.
But let's be honest—that approach is fundamentally broken.
Every time you send or receive money, you're hit with a poor exchange rate that has a hidden markup—the spread—baked right in. On top of that, you’re often stung with high SWIFT fees. This outdated system lacks any real transparency and puts your business at a serious financial disadvantage right from the start. It’s time for a smarter way forward, one built for the speed and clarity that modern businesses need.
The Modern Alternative for Business Forex
The good news? Financial technology has stepped in with a powerful alternative. Modern platforms like Zaro were built from the ground up to solve the very problems that cause businesses to overpay and lose control of their international transactions. Instead of a system that profits from confusion, you get a tool designed to deliver clarity and genuine cost savings.
This isn't just a small tweak; it's a complete rethink of how you manage money across borders. By stepping away from the old banking model, you can finally access the kind of tools and rates that large corporations have been using for years, effectively levelling the playing field for your SME.
This shift couldn't come at a better time. South African SMEs have lost money to non-transparent forex fees for far too long, but the market is changing. In fact, the South African forex market is projected to grow at a 6.58% compound annual rate, driven by growing trade and the move to digital. With daily turnover now exceeding $20 billion, electronic platforms are becoming essential for cutting costs and finding liquidity, especially in the all-important USD/ZAR pair. You can explore more insights into the growth of the South African foreign exchange market at IMARC Group.
Translating Features into Real-World Benefits
It’s easy to get lost in a list of features, so let's break down what these modern solutions actually mean for your day-to-day operations and, most importantly, your bottom line. Each feature is designed to fix a specific headache that businesses constantly face with international payments.
- Zero-Spread Exchange Rates: This is the game-changer. It means you get the real, live spot rate without any hidden markup. You immediately stop overpaying on every single transaction, which translates to direct and instant savings.
- No SWIFT or Hidden Fees: Say goodbye to those frustrating and unpredictable fees that banks tack onto international transfers. What you see is what you pay, giving you complete certainty over your costs and making financial planning much easier.
- Streamlined Digital Onboarding: Forget weeks of paperwork and trips to the bank. A secure digital Know Your Business (KYB) process means you can get your business account set up and ready to go in a matter of hours, not weeks.
- Multi-Currency Accounts: This gives you the power to hold, manage, and pay funds in both ZAR and USD. It allows you to receive payments from international clients without being forced into converting them immediately at whatever rate the bank gives you that day.
When you put these together, you get a much more efficient and cost-effective system.
By eliminating the spread and unnecessary fees, a modern fintech platform gives you direct access to the real forex market, fundamentally changing the economics of your international business.
Gaining Complete Control and Visibility
Beyond just saving money, the right platform gives your business the tools to manage your finances with real precision. This becomes even more critical as your team grows and your international footprint expands.
Enterprise-grade controls let you decide who on your team can access funds and what they can do with them. You can set custom permissions, create payment approval workflows, and track all spending in real-time. This level of visibility and control gives you complete oversight of your company's cash flow, seriously reducing the risk of mistakes or unauthorised transactions.
Ultimately, this modern approach is about more than just cheaper payments. It’s about arming your business with a financial tool that cuts down on admin, provides crystal-clear transparency, and gives you the control you need to protect your profits on the global stage. This is how you move from just surviving the challenges of forex to actually using it as a strategic advantage.
Your Practical Action Plan for Smarter Forex
Alright, enough with the theory. Let's get down to what really matters: taking control of your business’s foreign exchange costs. You don't need to become a full-time currency trader to stop bleeding money on international payments. What you need is a straightforward action plan to shift from passively accepting bank fees to actively managing your forex for a healthier bottom line.
Think of this as a roadmap. It’s designed to guide you away from the old, expensive way of doing things and towards a smarter approach that puts your business first. Making a few key changes here can have a massive, lasting impact on your cash flow and profitability.
Step 1: Start with a Simple Invoice Audit
Your first move is to figure out what you’re actually paying right now. It's often more than you think.
Grab a recent international invoice – one from a supplier you paid, or one a client settled. Now, find the exchange rate your bank gave you and compare it to the official mid-market rate for that day (a quick Google search will tell you). That gap you see? That’s the spread – the bank’s hidden profit margin.
Tack on any "international transfer" or "SWIFT" fees they charged, and suddenly you have a clear, honest number for what that single transaction truly cost you.
Step 2: Map Your Currency Exposure
Next, let's pinpoint where your business is most vulnerable to the whims of the currency market. This is simpler than it sounds. Just make a quick list of your regular international transactions.
- Inflows: Which clients are paying you in foreign currencies like US Dollars, Euros, or British Pounds?
- Outflows: Which suppliers, software subscriptions, or contractors do you pay in currencies other than the Rand?
This simple exercise reveals your currency exposure. It shows you exactly which transactions are at the mercy of market volatility and helps you see where you need to focus first. You’ll quickly identify the currency pairs that have the biggest impact on your financial health.
By auditing a past transaction and mapping your exposure, you turn an abstract problem ("forex risk") into a tangible number. That number represents the direct savings you can make by switching to a better solution.
Step 3: Explore Modern Forex Platforms
Armed with a clear picture of your costs and risks, it’s time to find a better way. To put your new strategy into action, you'll need the right tools, so understanding the best trading platform for beginners in South Africa is a crucial next step.
Look for platforms built specifically for businesses like yours, focusing on features that solve the problems you just uncovered.
Prioritise platforms that offer zero-spread exchange rates, as this immediately cuts out the biggest hidden cost. Also, make sure they have a clear, upfront fee structure and provide tools like multi-currency accounts, which give you far more control over your money.
The goal is to find a partner that values transparency and efficiency. A smooth, digital onboarding process means you can be set up and transacting at real exchange rates in no time. Taking these steps is the foundation for serious cost savings and a much more resilient financial future for your business.
Your Forex Questions, Answered
Jumping into the world of foreign exchange can feel a bit daunting, especially when your main focus is running your business. Let's tackle some of the most common questions South African business owners have, breaking it all down in simple terms.
Is Managing Forex Myself Too Risky for a Small Business?
It’s a fair question, but there’s a massive difference between speculative forex trading and practical forex management for your business. You’re not trying to bet on which way the rand will go. Your goal is much simpler: control your costs and lock in your profits.
Think of it this way: using a modern fintech platform is actually the least risky option. Sticking with a traditional bank and just accepting whatever rate they give you—along with their hidden fees—is where the real risk lies. Taking control means you secure the real exchange rate, protect your margins, and remove the guesswork.
How Is a Fintech Platform Different from My Bank?
It really boils down to two things: transparency and cost.
When you do a forex transaction with a traditional bank, they often add a significant markup to the exchange rate. This is their 'spread', and it's how they make a profit. On top of that, you'll likely get hit with hefty international transfer fees (like SWIFT fees) that chip away at your funds.
A dedicated fintech platform flips this model on its head. It’s built to give you direct access to the live, real-time exchange rate without the padded spread and hidden costs. This means what you see is what you get, and a lot more of your money stays where it belongs—in your business.
How Long Does It Take to Get Started?
Forget the old days of endless paperwork and queuing at the bank. Getting set up on a modern platform is surprisingly quick and painless.
Most use a slick, secure digital verification process (often called Know Your Business or KYB) that lets you do everything online. You can usually get your business verified and onboarded in a very short time. Once you're approved, you can fund your account and start making smarter, cheaper international payments right away.
Ready to take control of your international payments? With Zaro, you can stop losing money to hidden fees and unpredictable exchange rates. Get access to zero-spread forex and start saving on every single transaction. Learn more and sign up today at Zaro.
