Navigating the Forex Market with Confidence
This listicle provides eight essential forex risk management strategies to protect your capital and improve trading performance. For South African businesses, effectively managing forex risk is crucial for profitability. Learn how strategies like position sizing, stop-loss orders, diversification, hedging, risk-reward ratios, currency correlation analysis, using economic calendars, and trailing stops can mitigate your exposure to currency fluctuations. These forex risk management strategies empower you to navigate market volatility and optimize your forex transactions. For efficient and cost-effective international payments, consider Zaro, a platform designed for South African businesses.
1. Position Sizing Strategy
Position sizing is arguably the most crucial forex risk management strategy for South African businesses engaged in international trade. It’s the cornerstone of preserving capital and achieving consistent growth in the volatile foreign exchange market. This fundamental technique determines how much of your capital to allocate to each trade, ensuring that no single adverse market movement can cripple your business. It's not about picking winning trades every time; it’s about managing the inevitable losses so that they don't erase your gains and jeopardize your financial stability. This strategy is especially critical for South African businesses navigating the fluctuating Rand and dealing with international currencies.
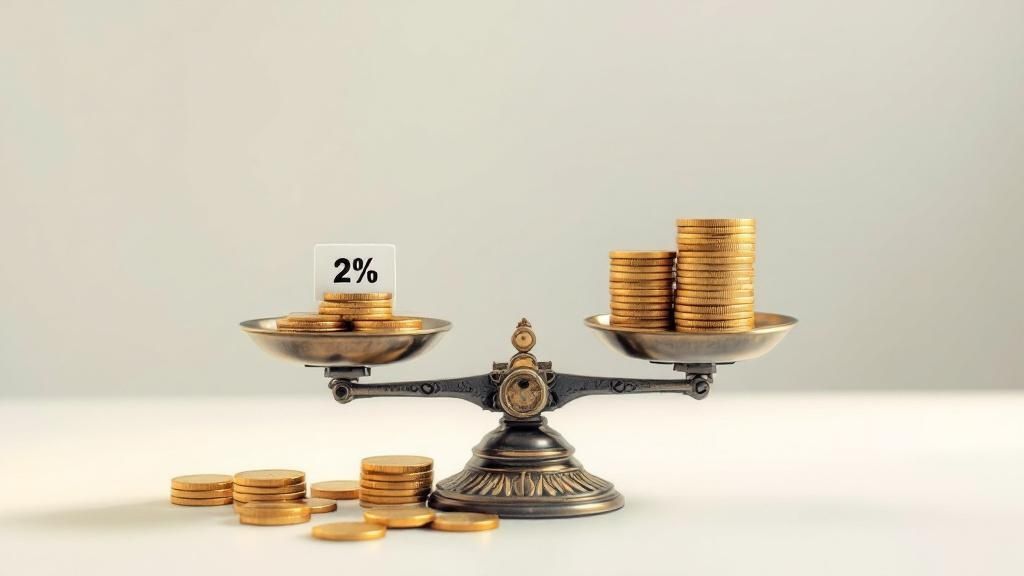

The core of position sizing revolves around percentage-based risk allocation. Instead of arbitrarily deciding how much Rand to exchange, you determine the acceptable risk for each trade as a percentage of your total trading capital. A common recommendation is to risk between 1-3% per trade, although more conservative traders, particularly professional fund managers and institutional forex desks, often opt for 0.5-1%. This means that for a business with R1 million in trading capital, a 2% risk equates to R20,000 per trade.
This percentage then dictates the size of your position based on your stop-loss order, a predetermined exit point that limits potential losses. A tighter stop-loss allows for a larger position size, while a wider stop-loss necessitates a smaller position. This dynamic adjustment ensures consistent risk management across different currency pairs and varying market conditions. For instance, a volatile pair like USD/ZAR might require a wider stop-loss and consequently a smaller position size compared to a less volatile pair.
Benefits for South African Businesses:
For South African businesses, particularly small and medium-sized export companies, CFOs seeking FX transparency, and BPO businesses managing international payments, position sizing provides significant advantages:
- Protection against Catastrophic Losses: The fluctuating Rand can expose businesses to significant currency risk. Position sizing acts as a buffer against unforeseen market shocks, preventing a single bad trade from severely impacting your bottom line.
- Consistent Risk Management: It provides a structured approach to managing forex exposure, promoting financial discipline and reducing the likelihood of impulsive, emotionally-driven trading decisions.
- Preservation of Capital: Consistent risk management, especially during losing streaks, allows South African businesses to weather market volatility and preserve their capital for future opportunities.
- Facilitates Compound Growth: By protecting capital, position sizing creates a foundation for steady, long-term growth through compounding returns.
Pros and Cons:
While highly effective, position sizing does have its limitations:
Pros: Protects against catastrophic losses, enables consistent risk management, preserves capital, facilitates compound growth, and reduces emotional stress.
Cons: May limit potential profits on high-conviction trades, requires strict adherence to pre-determined sizes, can be initially complex for beginners, and may result in small positions for businesses with limited trading capital.
Actionable Tips:
- Utilize Position Size Calculators: Several online tools automate the calculation process, simplifying position sizing for South African businesses.
- Never Risk More Than You Can Afford to Lose: This fundamental rule of trading is paramount to long-term survival in the forex market.
- Adjust for Volatility: Factor in market volatility when determining stop-loss distances and position sizes. Periods of high volatility warrant wider stops and smaller positions.
- Consider Correlation: If trading multiple currency pairs, consider the correlation between them. Highly correlated pairs can magnify risk, necessitating adjustments to overall position sizes.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your risk percentage based on your performance and market conditions.
Position sizing, championed by figures like Van Tharp and practiced by professional prop trading firms and institutional forex desks, is not merely a technique but a critical mindset shift. For South African businesses operating in the global marketplace, adopting a disciplined approach to position sizing is essential for mitigating forex risk, protecting capital, and achieving sustainable growth.
2. Stop-Loss Orders Strategy
In the volatile world of forex trading, managing risk is paramount, especially for South African businesses exposed to currency fluctuations. A cornerstone of effective forex risk management strategies is the implementation of stop-loss orders. This powerful tool allows traders, including South African businesses managing their FX exposure, to predefine acceptable loss limits on each trade, thereby protecting their capital from significant erosion. Stop-loss orders work by automatically closing a position when the market moves adversely by a specified amount. This automated execution removes the emotional element from loss-cutting decisions, a crucial factor for maintaining discipline and rational decision-making in the face of potential losses.
Stop-loss orders offer a high degree of flexibility in their implementation. They can be set at fixed price levels, as a percentage of the initial investment, or even based on dynamic technical analysis indicators like the Average True Range (ATR). This adaptability makes them suitable for various trading styles, from short-term day trading to longer-term swing trading. Furthermore, stop-loss orders can be implemented as either market orders, which execute at the prevailing market price when the stop level is triggered, or as limit orders, guaranteeing a minimum execution price but with the risk of the order not being filled if the market moves rapidly. The ability to adjust stop-loss levels as a trade moves favorably, known as trailing stops, further enhances their utility, locking in profits while still allowing for potential further gains. This 24/7 functionality is particularly relevant for South African businesses dealing with international currencies across different time zones.
The benefits of using stop-loss orders within a broader forex risk management strategy are numerous. They eliminate emotional decision-making, which often leads to holding onto losing positions for too long. By providing precise risk control for each trade, they allow traders and businesses to quantify their potential losses and allocate capital accordingly. This is crucial for South African CFOs seeking greater FX transparency and control. The automated nature of stop-loss orders also frees up time, allowing traders to step away from their screens without constantly monitoring positions. Critically, they prevent small losses from snowballing into devastating ones, preserving capital for future trading opportunities. For South African export companies and BPO businesses managing international payments, this can be the difference between maintaining profitability and incurring significant losses due to adverse currency movements.
However, stop-loss orders are not without their drawbacks. They can be triggered by temporary market spikes, a phenomenon known as "stop hunting," where large market participants intentionally push prices to trigger stop-loss orders and then capitalize on the resulting price movement. They can also lead to premature exits from trades during periods of normal market volatility. Slippage, the difference between the expected execution price and the actual price at which the order is filled, can occur, particularly during periods of high volatility. Fixed stop-loss levels may not be suitable for changing market conditions, and overly tight stops can reduce the overall winning percentage by prematurely exiting potentially profitable trades.
Despite these potential downsides, stop-loss orders remain an indispensable tool for forex risk management. South African businesses can leverage them effectively by implementing a few key strategies. Placing stops beyond significant support and resistance levels can minimize the risk of stop hunting. Using guaranteed stops, offered by some brokers, provides absolute protection during high-impact news events. Considering market volatility when setting stop distances is crucial, and traders should avoid moving stops against their positions, as this can magnify losses. Testing different stop-loss methods, such as fixed pips, percentage-based stops, or ATR-based stops, is vital to find the approach that best suits individual trading styles and risk tolerance.
The use of stop-loss orders has a rich history, dating back to technical analysis pioneers like Charles Dow and Jesse Livermore. Today, they are integral components of modern algorithmic trading systems and are offered as standard risk management tools by most forex brokers. For South African businesses navigating the complexities of the forex market, integrating stop-loss orders into a comprehensive risk management strategy is essential for protecting capital, maintaining discipline, and achieving long-term success in international trade.
3. Diversification Strategy
In the volatile world of forex trading, managing risk is paramount, especially for South African businesses exposed to currency fluctuations. Diversification is a core forex risk management strategy that involves spreading your risk across multiple currency pairs, trading strategies, timeframes, and even market conditions. This approach aims to reduce your overall portfolio risk by leveraging the principle that different currency pairs don't always move in tandem. Losses incurred in one pair can potentially be offset by gains in another, leading to a more stable and predictable performance over time. This is particularly crucial for South African businesses operating in a globalized market, where currency volatility can significantly impact profit margins.

Diversification earns its place as a top forex risk management strategy due to its ability to mitigate the impact of unforeseen market events. For South African businesses, this could mean buffering against the effects of fluctuating commodity prices or changes in global economic sentiment. The strategy relies on strategically allocating resources across a range of uncorrelated currency pairs, combining different trading methodologies and timeframes, and even incorporating both major and minor currencies. This multi-pronged approach creates a safety net, preventing over-reliance on a single currency or market condition. For example, an exporter relying solely on USD income would be significantly impacted by a weakening dollar. Diversifying into other currencies like the Euro or British Pound could help offset potential losses. This diversified approach can also encompass exposure to different economic regions, offering further protection from localized economic downturns. Imagine a scenario where political instability in one region affects its currency. A diversified portfolio with exposure to other stable regions could mitigate the negative impact.
Successful implementation of a diversification strategy requires careful planning and analysis. For instance, a South African business might trade EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and AUD/CAD concurrently to diversify their geographical risk. They might also combine short-term scalping strategies on EUR/USD with longer-term swing trading on less volatile pairs like USD/ZAR. Hedge funds often maintain exposure across a basket of G10 currencies for broad diversification, while retail traders might employ currency basket approaches tailored to their specific risk tolerance. These examples illustrate how diversification can be tailored to various investment styles and risk profiles.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Diversification Strategy:
- Regularly Monitor Currency Correlations: Currency correlations can shift, especially during times of economic uncertainty. Utilize correlation analysis tools to understand the relationships between different currency pairs and adjust your portfolio accordingly. This is crucial for South African businesses as global economic events can significantly impact the ZAR and its correlations with other currencies.
- Limit Exposure to Any Single Currency: Avoid overexposure to any single currency, including the USD. A general guideline is to limit exposure to a maximum of 30% for any single currency. This mitigates the impact of sharp fluctuations in any one currency on your overall portfolio.
- Diversify Across Trading Sessions: Take advantage of the 24-hour forex market by spreading your trades across different trading sessions (Asian, European, and American). This can help capture opportunities in different markets and reduce the impact of overnight risk.
- Combine Different Trading Strategies: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket, strategically combine trend-following and mean-reversion strategies. This ensures that your portfolio is positioned to profit in various market conditions. For South African exporters, this could involve hedging against future ZAR fluctuations while also capitalizing on short-term market trends.
- Optimize Pair Selection with Correlation Analysis: Use correlation matrices and other analytical tools to identify currency pairs that exhibit low or negative correlation. This ensures that your diversification efforts are effective in reducing overall portfolio volatility.
Pros and Cons of Diversification:
Pros:
- Reduces overall portfolio volatility
- Provides multiple opportunities for profit
- Limits the impact of single currency or country events
- Smooths out the equity curve over time
- Allows trading in different market conditions
Cons:
- May dilute returns from best-performing strategies
- Requires more time and analysis for multiple positions
- Can increase complexity and monitoring requirements
- Some currency pairs may become correlated during crises
- Potentially higher transaction costs from multiple positions
Diversification is not a "set it and forget it" strategy. It requires ongoing monitoring, analysis, and adjustment. However, for South African businesses navigating the complexities of the forex market, the benefits of reduced risk and increased stability make diversification a vital tool in achieving long-term financial success. For South African CFOs, diversification provides increased FX transparency and allows for more predictable financial forecasting. For BPO businesses operating in South Africa, managing currency risk is crucial for maintaining profitability, and diversification provides a robust framework for achieving this.
4. Hedging Strategy
Hedging is a crucial forex risk management strategy that involves creating offsetting positions to mitigate potential losses from adverse currency fluctuations. It's like taking out an insurance policy against unfavorable market movements. Instead of solely relying on predictions, hedging allows businesses to control their forex exposure and protect their bottom line, especially in the volatile South African Rand (ZAR) market. This makes it an essential tool for South African businesses engaged in international trade, from small exporters to large multinational corporations.
Hedging works by establishing a position that moves in the opposite direction of your primary trade. For instance, if you're a South African exporter who has received USD and anticipates the ZAR strengthening against the USD in the coming months, you’re effectively holding a long ZAR/USD position (expecting the ZAR to appreciate). To hedge against the risk of the ZAR weakening instead, you would open a short ZAR/USD position. If the ZAR does indeed weaken, the loss on your initial USD holding would be offset by the gain on your short position. This limits your potential losses, although it also limits potential gains if the ZAR strengthens as originally anticipated.
Several hedging instruments are available in the forex market, including:
- Direct Hedging (using the same currency pair): This involves opening an opposite position in the same currency pair as your main trade. However, be aware that some brokers may not allow direct hedging due to regulatory restrictions.
- Indirect Hedging (using correlated currency pairs): If direct hedging is unavailable, you can use a correlated currency pair. For example, if a South African business has USD receivables, they might consider shorting EUR/ZAR as a partial hedge, leveraging the historical correlation between EUR/ZAR and USD/ZAR movements. This approach requires careful calculation of the hedge ratio to ensure effective risk mitigation.
- Derivatives (options, forwards, futures): These instruments offer more sophisticated hedging strategies. Options, for instance, provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. Forwards and futures contracts lock in exchange rates for future transactions, providing certainty for businesses. For South African businesses dealing with fluctuating commodity prices and exchange rates, these derivatives can offer valuable protection.
Hedging can be employed as a temporary or permanent strategy, offering either full or partial coverage depending on the risk appetite and specific needs of the business. For example, a business might choose to hedge only a portion of their forex exposure, balancing risk mitigation with potential profit. Another common use case is temporary hedging around specific events, such as earnings announcements or periods of heightened market volatility, like during elections or economic announcements impacting the ZAR.
Pros of Hedging:
- Insurance against adverse market moves: Protects against unexpected ZAR fluctuations.
- Maintain positions during uncertain times: Enables businesses to hold onto existing positions without being forced to liquidate due to short-term market volatility.
- Reduce portfolio volatility: Creates greater predictability in cash flows, especially crucial for South African businesses operating in volatile emerging markets.
- Enable trading during high-impact news events: Offers stability during potentially disruptive market periods.
- Flexibility in risk management timing: Allows businesses to hedge proactively before anticipated events.
Cons of Hedging:
- Reduces profit potential from favorable moves: Caps potential gains if the market moves in your favor.
- Increases transaction costs and spread expenses: Each hedging transaction incurs costs, potentially impacting overall profitability.
- May create complex position management: Requires diligent tracking and monitoring of multiple positions.
- Some brokers don't allow direct hedging: Limits hedging options and might necessitate using correlated pairs.
- Can lead to overconfidence and larger position sizes: The perceived safety net of hedging may encourage excessive risk-taking.
Tips for Effective Hedging:
- Calculate hedge ratios for correlated pairs carefully: Incorrect ratios can leave you under-hedged or over-hedged.
- Consider the cost of hedging versus potential loss: Evaluate the cost-benefit relationship to determine the optimal hedging strategy.
- Use hedging for specific events rather than a permanent strategy: Continuous hedging can erode profits over the long term.
- Monitor correlation stability between hedge instruments: Correlations can change over time, impacting the effectiveness of your hedge.
- Plan your hedge exit strategy in advance: Define clear criteria for unwinding your hedge position.
Hedging is a powerful tool for managing forex risk, particularly relevant for South African businesses exposed to ZAR volatility. By understanding the different hedging techniques and applying them strategically, businesses can navigate the complexities of the forex market and safeguard their financial performance. While hedging has its costs, the stability and peace of mind it provides can be invaluable for businesses operating in the often-turbulent world of international trade.
5. Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy
One of the most crucial forex risk management strategies for South African businesses, especially small and medium-sized export companies dealing with fluctuating exchange rates, is the Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy. This method provides a structured approach to managing potential losses and maximizing profits in the volatile forex market, offering a degree of predictability crucial for financial planning and stability. This strategy deserves its place on this list because it directly addresses the core challenge of forex trading: balancing the inherent risks with the potential for reward. By implementing this strategy effectively, businesses can significantly improve their odds of consistent profitability and mitigate the impact of adverse currency movements.
The Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy essentially involves pre-defining the potential profit relative to the potential loss for every trade you consider. This is expressed as a ratio, with common ratios being 1:2, 1:3, or even higher. For example, a 1:2 ratio means you're aiming to make R2 for every R1 you're risking. This methodical approach allows you to prioritize quality trades over quantity, focusing on setups that offer a significant potential return for the level of risk undertaken. This is particularly important for South African businesses operating in the often turbulent emerging markets landscape.
How it Works:
The strategy combines two key components: a predetermined profit target and a stop-loss level. Before entering a trade, you identify your stop-loss, which is the point at which you'll exit the trade to limit potential losses. Your profit target is then set at a multiple of your stop-loss, according to your chosen risk-reward ratio. For instance, with a 50-pip stop-loss and a desired 1:2 ratio, your profit target would be 100 pips. This structured approach allows for complete trade planning and promotes a disciplined, rather than emotional, approach to forex trading.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
The Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy is employed by various market participants, demonstrating its effectiveness across different trading styles. Professional prop traders, for instance, often utilize this strategy, even achieving profitability with win rates below 50% by leveraging ratios of 1:3 or higher. Imagine a South African exporter who adopts a 1:3 ratio. Even if only 40% of their currency trades are successful, they can still remain profitable because their winning trades generate significantly larger returns than their losing trades. Similarly, hedge funds frequently incorporate asymmetric risk-reward profiles in currency carry trades, aiming to capture small, consistent gains while minimizing potential downside. Even algorithmic trading systems, widely used in the forex market, are often programmed with minimum risk-reward thresholds, highlighting the importance of this strategy in automated trading environments.
Actionable Tips for South African Businesses:
- Adjust Ratios Based on Volatility: The South African Rand can be volatile. During periods of heightened volatility, consider using more conservative ratios (e.g., 1:2) to account for increased risk. In calmer markets, you might explore higher ratios.
- Use Technical Analysis: Employ technical analysis tools to identify realistic profit targets based on historical price movements and support/resistance levels.
- Track Your Performance: Monitor your average risk-reward ratio over time to assess the effectiveness of your strategy and identify areas for improvement.
- Partial Profit-Taking: Consider implementing a partial profit-taking strategy. This involves securing a portion of your profits at predetermined levels, improving your overall win rate while still allowing for potential further gains.
- Focus on Trade Setups: Identify trade setups that naturally offer favourable risk-reward ratios. Don’t force trades that don’t meet your criteria.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Profitability even with lower win rates
- Encourages disciplined trade selection
- Clear profit and loss expectations
- Enhanced emotional discipline
- Consistent trading approach
Cons:
- May miss some profitable trades
- Requires patience for ideal setups
- Market conditions may not always align with target ratios
- Fixed ratios might not suit all market situations
- Potential for missed opportunities in strongly trending markets
The Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy is a powerful tool for South African businesses navigating the complexities of forex. By understanding and implementing this strategy, businesses can enhance their forex risk management, fostering a more disciplined and potentially more profitable approach to currency trading. While no strategy guarantees success, the Risk-Reward Ratio approach offers a structured framework for managing risk and maximizing potential returns in the dynamic world of forex.
6. Currency Correlation Analysis Strategy
Managing forex risk effectively is crucial for any business involved in international trade, and this is particularly true for South African companies operating in the global marketplace. Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact profitability, making robust risk management strategies essential. One such strategy, currency correlation analysis, offers a powerful tool for mitigating risk and optimizing returns. This strategy deserves its place on this list because it allows businesses to gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of currency markets, ultimately enabling more informed and strategic decision-making.
Currency correlation analysis involves examining the statistical relationship between different currency pairs. It measures how two currencies move in relation to each other over a specific period. This relationship is quantified by a correlation coefficient, ranging from -1.0 to +1.0. A coefficient of +1.0 indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning the two currency pairs move in tandem. Conversely, a coefficient of -1.0 represents a perfect negative correlation, where the pairs move inversely. A coefficient of 0 indicates no discernible relationship. Understanding these relationships is key to effective forex risk management strategies.
This strategy is particularly relevant for South African businesses dealing with multiple currencies, such as USD, EUR, GBP, and perhaps even the ZAR against other emerging market currencies. For instance, the South African Rand often exhibits correlations with other commodity-linked currencies. Understanding these links can provide valuable insights for managing currency risk.
How Currency Correlation Analysis Works in Practice:
Let's say a South African exporter receives payments in USD and incurs expenses in EUR. By analyzing the correlation between USD/ZAR and EUR/ZAR, they can assess their net exposure. If these pairs are highly positively correlated, a strengthening Rand would benefit both sides of the equation, reducing both income and expenses in ZAR terms. However, a weakening Rand would negatively impact both, increasing costs and reducing the ZAR value of USD income. This understanding allows businesses to make more informed hedging decisions.
Benefits of Implementing Currency Correlation Analysis:
- Prevents Overexposure: By understanding how different currencies move together, businesses can avoid inadvertently concentrating their risk in similar assets. For example, holding positions in highly correlated currencies like EUR/USD and GBP/USD can effectively double a company’s exposure to the USD. Correlation analysis helps avoid such scenarios.
- Optimizes Portfolio Diversification: This strategy assists in constructing a diversified portfolio by identifying currency pairs that offer genuine diversification benefits. This is especially valuable for South African businesses managing multiple currency exposures.
- Identifies Natural Hedging Opportunities: Negative correlations can create natural hedges. For example, if a South African company receives income in USD and has expenses in CHF, and the USD/ZAR and CHF/ZAR have a negative correlation, fluctuations in the Rand might be offset by opposing movements in these currency pairs, providing a natural hedge.
- Improves Understanding of Market Relationships: Currency correlation analysis allows businesses to gain a deeper understanding of the complex interplay of factors influencing currency movements.
Potential Drawbacks:
While powerful, currency correlation analysis has limitations:
- Correlations Change: Economic conditions and market sentiment can cause correlations to shift, even dramatically, as seen during the 2008 financial crisis. Regular monitoring and adjustments are crucial.
- Historical Data Isn't Foolproof: Past correlations don’t guarantee future relationships. Relying solely on historical data can be misleading.
- Complexity: Analyzing numerous currency pairs can become complex and require specialized tools.
Actionable Tips for South African Businesses:
- Focus on the Short-Term: Use 30-day rolling correlations for insights into current market dynamics.
- Monitor Different Market Regimes: Observe how correlations behave during periods of high volatility versus periods of stability.
- Look for Breakdowns: Significant shifts in established correlations can present trading or hedging opportunities.
- Stress Test Your Portfolio: Use correlation analysis to assess how your portfolio might perform under various market scenarios.
Examples of Correlations:
- EUR/USD and GBP/USD typically show a strong positive correlation.
- USD/CHF and EUR/USD often exhibit a negative correlation, particularly during periods of risk aversion where the CHF acts as a safe haven.
- Commodity currencies like AUD/USD, CAD/USD, and NZD/USD often demonstrate positive correlations during periods of risk appetite or aversion.
By incorporating currency correlation analysis into their forex risk management strategies, South African businesses can gain a significant edge in navigating the complexities of the global currency market. While it requires diligent monitoring and understanding, the potential benefits for enhancing risk management and optimizing returns are substantial.
7. Economic Calendar and News Risk Management
Navigating the forex market requires a keen awareness of the dynamic forces that shape currency valuations. Among the most potent of these forces is news. Economic announcements, central bank pronouncements, and geopolitical events can trigger significant market volatility, creating both opportunities and risks for forex traders. For South African businesses engaged in international trade, understanding and managing news risk is a critical component of a robust forex risk management strategy. This is particularly true for small and medium-sized export companies, business owners, executives, CFOs seeking FX transparency, and BPO businesses operating in South Africa, all of whom are exposed to the fluctuations of the Rand. Effective news risk management can help protect your bottom line and ensure predictable financial performance.
Economic Calendar and News Risk Management is a forex risk management strategy that involves actively monitoring and preparing for scheduled economic releases, central bank announcements, and geopolitical events that have the potential to cause significant market movements. This approach acknowledges that news can inject substantial volatility into the forex market, leading to rapid price swings and potentially widening spreads. Instead of being caught off guard, traders utilizing this strategy aim to anticipate these periods of heightened volatility and adjust their trading behavior accordingly. This can range from adjusting position sizes and stop-loss orders to completely avoiding trading during particularly sensitive periods.
How it Works:
This strategy revolves around the use of economic calendars, which provide schedules of upcoming economic data releases, central bank meetings, and other significant events. These calendars often include an assessment of the potential impact of each event (high/medium/low), allowing traders to prioritize their attention. By staying informed about these scheduled events and their potential impact on the ZAR and other relevant currencies, businesses can anticipate periods of increased volatility.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Reducing Position Sizes Before Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) Releases: The NFP report, a key indicator of the US labor market, often causes significant USD volatility. A South African exporter with USD receivables might reduce their USD exposure before the NFP release to mitigate potential losses from a sudden Rand appreciation.
- Closing Positions Before South African Reserve Bank (SARB) Meetings: SARB interest rate decisions can dramatically impact the Rand. A business might choose to close out ZAR positions before these meetings to avoid being caught in a volatile price swing.
- Using Wider Stops During ECB Press Conferences: If a South African business is exposed to the Euro, widening stop-loss orders during ECB press conferences can help protect against losses stemming from unexpected announcements.
Actionable Tips for South African Businesses:
- Utilize Economic Calendars with Impact Ratings: Subscribe to a reputable economic calendar that categorizes events by their potential impact. Pay close attention to events affecting the ZAR and your trading counterparties.
- Set Alerts for Relevant Events: Configure alerts for upcoming high-impact news events related to your traded currencies. This allows you to react promptly and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Practice Trading News Events in Demo Accounts: If you are new to news trading, practice your strategies in a demo account before implementing them in a live trading environment.
- Consider Time Zone Differences: Be aware of the time zones for global news releases. Schedule your monitoring accordingly to ensure you are prepared for potentially market-moving events.
- Develop Specific Protocols for Different News Events: Establish clear protocols for managing risk around different types of news events (e.g., interest rate decisions, inflation reports, geopolitical developments).
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This strategy is particularly valuable for businesses with significant forex exposure who want to proactively manage risk. It's essential for:
- Managing Volatility: News events can create sharp and unpredictable price movements. This strategy helps mitigate the risk of substantial losses during these volatile periods.
- Improving Forecasting: Understanding the potential impact of upcoming news allows businesses to better anticipate market movements and make more informed decisions.
- Enhancing Strategic Planning: By incorporating news analysis into their forex risk management strategy, businesses can develop more robust and adaptable plans.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Prevents unexpected losses, helps time entries and exits, provides market context, enables proactive risk management, improves understanding of market drivers.
Cons: May cause missed opportunities, requires constant monitoring, news impact can be unpredictable, can lead to overanalysis, high-impact events occur frequently.
This strategy deserves a prominent place in any forex risk management toolkit. By understanding and effectively managing news risk, South African businesses can navigate the complexities of the forex market with greater confidence and protect their financial interests.
8. Trailing Stop Strategy: Locking in Forex Profits While Managing Risk
For South African businesses navigating the complexities of forex, effective risk management is paramount. Fluctuations in the Rand can significantly impact profitability, making strategies like the trailing stop an essential tool in any forex risk management arsenal. This dynamic approach offers a powerful way to protect profits while still allowing for potential gains during favorable market movements, a particularly crucial advantage for South African exporters and importers dealing with volatile currency pairs. It deserves its place on this list because it offers a practical, adaptable solution for businesses of all sizes to mitigate forex risk and enhance financial stability.
The trailing stop strategy employs a dynamic stop-loss order that automatically adjusts to follow the market price as it moves in your favor. Think of it as a safety net that moves higher as your profits grow. Unlike a traditional stop-loss order, which remains fixed at a specific price point, the trailing stop "trails" the market price by a pre-determined distance, whether it's a fixed number of pips or a percentage of the current price. Crucially, the stop-loss never moves against your position; it only moves in the direction of profit, locking in gains as the trade progresses. This dynamic adjustment allows you to capture gains from extended trends, a common occurrence in currency pairs involving the South African Rand, without the constant worry of manually adjusting your stop-loss.
How it Works in Practice:
Imagine a South African exporter selling goods to the US. They receive payment in USD and need to convert it to ZAR. They decide to use a trailing stop to protect their profits from a potential drop in the USD/ZAR exchange rate. Let's say the current exchange rate is 18.00 ZAR/USD, and they set a 50-pip trailing stop. This means the initial stop-loss is placed at 17.95. If the USD/ZAR rate moves up to 18.10, the trailing stop will automatically adjust to 18.05, locking in a 50-pip profit. This process continues as long as the market moves favorably. If the USD/ZAR rate suddenly reverses and drops to 18.05, triggering the trailing stop, the trade is closed, and the exporter secures their profit.
Successful Implementation Examples:
- Percentage-Based Trailing Stop: A South African importer buying goods from Europe might use a 2% trailing stop on the EUR/ZAR exchange rate. This adjusts the stop-loss dynamically based on the current market price, providing a flexible approach to managing risk in a fluctuating market.
- Moving Average as a Reference: A CFO managing forex exposure for their company could use a 20-period moving average as a dynamic trailing stop reference. If the exchange rate falls below the moving average, the trailing stop is triggered, protecting against significant losses. This approach is particularly helpful in trending markets.
- Volatility Adjustment: South African hedge funds often employ Average True Range (ATR)-based trailing stops. ATR measures market volatility, allowing for wider trailing stops during volatile periods and tighter stops during calmer periods. This adaptability is essential for managing risk effectively in the often-volatile South African forex market.
Actionable Tips for South African Businesses:
- Wider Stops in Volatile Markets: Given the potential for volatility in emerging market currencies like the Rand, using wider trailing distances, especially during periods of economic uncertainty or news releases, can prevent premature exits.
- Consider Market Structure: Analyze the typical price movements of the currency pair you are trading. Trending pairs might benefit from wider stops, while range-bound pairs might require tighter stops.
- Combine with Technical Analysis: Use technical indicators like support and resistance levels to optimize trailing stop placement. This approach enhances the strategy's effectiveness and allows for more strategic profit capture.
- Backtesting: Test different trailing methods and parameters on historical data to find the optimal settings for your specific trading style and risk tolerance.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Locks in profits progressively during favorable market movements.
- Allows participation in extended trends without constant monitoring.
- Removes emotion from profit-taking decisions.
- Provides downside protection throughout the trade duration.
- Can significantly improve risk-adjusted returns.
Cons:
- May exit trades prematurely during normal market retracements.
- Can be triggered by temporary market noise or short-term fluctuations.
- Fixed trailing distances may not suit all market conditions.
- Requires careful calibration to balance protection and profit capture.
The trailing stop strategy provides a robust mechanism for South African businesses to manage forex risk effectively. Its ability to lock in profits while still allowing for potential upside makes it a valuable tool for exporters, importers, and any business with foreign currency exposure. By understanding its nuances and applying it strategically, businesses can enhance their forex trading outcomes and protect their bottom line.
Forex Risk Management Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position Sizing Strategy | Medium - requires calculations and discipline | Low to Medium - needs position size tools | Consistent risk management and capital preservation | All traders managing risk and capital allocation | Protects against large losses; supports compound growth |
| Stop-Loss Orders Strategy | Low - preset exit points, easy to automate | Low - standard broker tools available | Limited losses and disciplined exit | Any trading style needing automated risk control | Removes emotion from loss-cutting; precise risk limits |
| Diversification Strategy | Medium to High - managing multiple assets | Medium to High - requires monitoring multiple positions | Reduced portfolio volatility and smoother performance | Portfolio traders seeking risk spread across currencies | Limits single event impact; multiple profit opportunities |
| Hedging Strategy | High - complex position management | Medium to High - may involve derivatives | Risk reduction and portfolio insurance | Protecting positions during uncertain or volatile markets | Enables risk neutralization; flexible risk management |
| Risk-Reward Ratio Strategy | Medium - requires planning and patience | Low - mainly discipline and trade planning | Long-term profitability even with lower win rates | Traders focusing on quality setups and disciplined exits | Encourages disciplined trading; clear profit targets |
| Currency Correlation Analysis Strategy | High - requires statistical analysis and monitoring | Medium - correlation tools and data analysis | Optimized diversification and reduced overexposure | Portfolio managers avoiding correlated risk buildup | Improves diversification; identifies natural hedges |
| Economic Calendar and News Risk Management | Medium - requires event tracking | Low to Medium - calendar tools and news feeds | Avoids unexpected volatility, better trade timing | Traders sensitive to fundamental events and news volatility | Prevents surprise losses; proactive risk adjustments |
| Trailing Stop Strategy | Low to Medium - setting dynamic stops | Low - broker platform features available | Protects profits while allowing trend participation | Trend followers capturing extended moves | Locks profits; reduces emotional profit-taking decisions |
Mastering Forex Risk: Your Path to Sustainable Trading
Successfully navigating the forex market requires a robust understanding of and commitment to forex risk management strategies. This article has outlined eight key strategies, from position sizing and stop-loss orders to diversification and hedging, that are crucial for mitigating potential losses and preserving your capital. We also explored the importance of understanding currency correlations, utilizing economic calendars, implementing trailing stops, and carefully calculating your risk-reward ratio. By mastering these concepts, South African businesses, from SMEs to large corporations, can significantly improve their trading outcomes and protect themselves against volatile currency fluctuations. This is especially crucial for businesses operating within the ZA region, where fluctuating exchange rates can significantly impact profitability.
The most important takeaway is that consistent profitability in forex isn't solely about identifying winning trades; it's about managing the risk associated with those trades. By diligently applying these forex risk management strategies, you'll not only protect your investments but also gain the confidence to make informed trading decisions, setting you on a path towards sustainable growth and success in the international market. For South African businesses looking to further enhance their forex risk management, consider exploring platforms like Zaro. Zaro offers streamlined and cost-effective solutions for managing international payments, helping you minimize forex risk and optimize your bottom line. Visit Zaro today to discover how they can empower your business in the global marketplace.
