Understanding the New Reality of International Money Transfers

The landscape of international money transfers has undergone a significant transformation. Selecting the optimal method for sending money across borders now demands more than a simple fee comparison. It requires a nuanced understanding of the operational mechanics of banks, forex brokers, and fintech platforms such as Zaro. We need to look beyond the surface and delve into the core of their respective business models.
Traditional banks, for instance, often rely on a complex web of correspondent banks. This network, while established, introduces intermediary fees that can be opaque and difficult to anticipate. Banks also generate revenue through the margin applied to the exchange rate. This seemingly small difference between their offered rate and the real-time market rate can significantly impact the final amount received. The inherent reliance on legacy systems and stringent regulatory compliance often translates to slower processing times. However, this established infrastructure does offer a sense of stability and established recourse mechanisms, making them a suitable option for high-value transfers where security is paramount.
Forex brokers, on the other hand, specialize in currency exchange. Their significant trading volumes and direct market access typically result in more competitive exchange rates. This makes them a popular choice for businesses managing substantial international transactions. Their expertise in navigating the complexities of fluctuating exchange rates can be invaluable. However, due diligence is essential: verifying their regulatory standing and understanding their specific service parameters, such as minimum transfer amounts, is crucial.
Fintech platforms employ technology to streamline the transfer process. Often, they can offer faster speeds and lower fees compared to traditional banks. This increased efficiency has captured a growing share of the market. The digital remittances market in South Africa, for example, is projected to reach US$513.44 million by 2025. Discover more insights This growth reflects a clear shift in consumer preference toward faster, more convenient solutions. However, understanding their security protocols and dispute resolution processes is paramount, especially in the dynamic and evolving fintech landscape. Choosing the right platform requires a holistic assessment of cost, speed, reliability, and the platform's ability to cater to your specific transfer needs.
Why Banks Cost More Than You Think (And When It's Worth It)
Banks often project an image of reliability, especially when it comes to international money transfers. They highlight their security measures and well-established processes. However, this sense of security often comes at a steep, and sometimes hidden, price. Understanding how banks structure their fees is essential for making smart decisions about sending money abroad.
One of the main reasons banks are more expensive is the correspondent banking network. This network relies on intermediary banks to facilitate transfers between different countries and currencies. Each intermediary bank deducts its own correspondent banking fees, increasing the overall cost. These fees are often unpredictable and aren't always clearly disclosed upfront. Furthermore, banks generally bake profit into the exchange rate margin. They offer a slightly worse exchange rate than the real-time market rate, pocketing the difference. This seemingly small margin can quickly add up, especially with larger transfers. Combined with the standard transfer fee, these hidden costs make using banks a pricier option.
South Africa's current position as the world's most expensive country for international money transfers further complicates the issue. Sending $200 from South Africa costs an average of 13.18%, nearly double the cost of the next most expensive G20 nation. This fact alone highlights the importance of carefully analyzing costs when choosing a method for sending money abroad. Discover more insights
Despite the higher costs, banks do have legitimate advantages in specific situations. For large transfers, the established infrastructure and regulatory compliance banks offer provide a level of security that can be worth the extra cost. Their well-developed systems and procedures give you better options for recourse if errors or disputes arise.
Moreover, banks typically have dedicated customer service teams knowledgeable about the complexities of international transfer regulations. They can offer tailored guidance for intricate transactions. This personalized support can be particularly helpful for businesses or individuals handling substantial financial transfers with specific compliance requirements.
Traditional Bank Transfer Cost Breakdown
The table below provides a comparison of international transfer fees, exchange rate margins, and other charges from major South African banks, revealing the potential total cost of sending money abroad.
| Bank | Transfer Fee | Exchange Rate Margin | Correspondent Bank Fee | Total Cost (R10,000 transfer) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | R150 | 1.5% | Varies (R200-R500) | R400 - R750 + R150 (Transfer Fee) |
| Bank B | R200 | 2.0% | Varies (R150-R400) | R350 - R600 + R200 (Transfer Fee) |
| Bank C | R100 | 1.0% | Varies (R250-R600) | R350 - R700 + R100 (Transfer Fee) |
Note: These figures are illustrative examples and can vary based on the specific bank and transfer details. Always confirm current fees directly with your bank.
As you can see, even small differences in fees and margins can significantly impact the overall cost. Correspondent bank fees, in particular, can be difficult to predict and add a layer of complexity to the cost calculation.
When considering using a bank for your transfer, transparency is paramount. Don't hesitate to ask specific questions about all possible fees, including correspondent bank charges and exchange rate margins. Be sure you understand the bank's liability in the event of delays or mistakes. By understanding the complete cost picture and evaluating it against your specific needs, you can make an informed decision. You can then determine whether the perceived security and established reputation of a bank justify the higher cost for your particular international money transfer needs.
Forex Brokers: When Currency Expertise Actually Matters

Forex brokers occupy a unique niche in the world of international money transfers. Their specialized knowledge of currency markets offers distinct advantages, especially when it comes to securing favorable exchange rates. This expertise, combined with high trading volumes and direct market access, often allows them to offer rates significantly better than traditional banks. This makes them particularly appealing to businesses frequently sending money abroad. However, this specialized approach also comes with its own set of considerations.
Understanding the Forex Broker Model
Forex brokers operate on a thin-margin, high-volume model. Their profits come from the small difference between the buying and selling price of currencies, amplified across a large number of transactions. This allows them to offer more competitive exchange rates than banks, which typically build in larger margins to cover operational costs. Furthermore, forex brokers generally bypass the often cumbersome and costly correspondent banking network, further reducing fees and potentially speeding up transfer times. This can be a significant advantage for time-sensitive transactions.
Verification and Regulation: Navigating the Landscape
While the allure of competitive rates and faster transfers is undeniable, choosing a forex broker requires due diligence. Verification procedures tend to be stricter than those of traditional banks. This reflects the increased risk of illicit activities like money laundering and fraud in the international currency market. Expect to provide comprehensive documentation, including proof of identity and address.
The regulatory environment for forex brokers also varies considerably between jurisdictions. Verifying a broker's regulatory standing in both your home country and the destination country is paramount. This confirmation ensures they are operating within legal parameters and offers a layer of protection should disputes arise.
Service Limitations and Hidden Costs: Beyond the Exchange Rate
Before opting for a forex broker, consider their specific service parameters. Many impose minimum transfer amounts, potentially excluding them as an option for smaller, personal remittances. Services might also be restricted to particular currencies or countries. While currency exchange is their core competency, they generally don't offer the wider array of financial services found at a traditional bank.
Lastly, be mindful of potential hidden fees. While perhaps less common than with banks, charges such as inactivity fees or fees tied to specific transfer methods can diminish the initial cost savings from a favorable exchange rate. A thorough review of the broker's fee schedule is essential before initiating any transfers.
To assist in your decision-making process, let's examine a comparison of several leading forex brokers.
Forex Broker Service Comparison
The following table provides a snapshot of key factors to consider when choosing a forex broker, including exchange rate margins, transfer speeds, minimum transfer amounts, customer support options, and regulatory status.
| Broker | Exchange Rate Margin | Transfer Speed | Minimum Transfer | Customer Support | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broker A | 0.5% - 1.5% | 1-3 business days | $500 | Phone, Email, Chat | Regulated by Regulatory Body A |
| Broker B | 0.3% - 1.2% | 0.5-2 business days | $1000 | Email, Chat | Regulated by Regulatory Body B |
| Broker C | 0.7% - 2.0% | 1-5 business days | $250 | Phone, Email | Regulated by Regulatory Body C |
This table provides a general overview and specific offerings can vary. Always consult the broker directly for the most up-to-date information.
By understanding the nuances of the forex broker model, including its advantages and limitations, you can make an informed decision about whether this route aligns with your specific international money transfer needs. Weighing factors like transfer frequency, amount, destination, and the importance of speed against security and regulatory compliance will allow you to select the optimal solution.
Fintech Revolution: Speed and Convenience With Hidden Costs
Fintech platforms like Zaro have undeniably reshaped international money transfers, emphasizing speed and convenience through user-friendly apps and websites. Their advertised lower fees compared to traditional banks are a major draw for customers looking for faster, more affordable options. But this apparent simplicity can sometimes obscure the complexities involved. Understanding the nuances of these platforms is critical for making informed choices.
The Mechanics of Fintech Transfers: Speed and Cost Optimization
Fintechs often achieve faster processing times by utilizing existing banking infrastructure. Partnering with local banks in different countries streamlines transfers, bypassing the sometimes cumbersome correspondent banking networks, known for delays and added fees. Zaro, for example, utilizes local accounts for both ZAR and USD, expediting transfers within this particular corridor. This technology-driven approach also minimizes operational overhead, contributing to the cost savings passed on to users.
Their competitive exchange rates frequently stem from high transaction volumes and algorithms designed to capitalize on real-time market fluctuations. Zaro's zero-spread model, which offers the true spot exchange rate, is a case in point. However, understanding how these companies generate profit without a margin on the exchange rate is crucial. Often, it's through volume-based pricing, subscription fees for premium features, or fees tied to specific transaction types like business payments or large transfers.
User Experience and Support: A Trade-off For Speed?
While fintech platforms generally offer sleek, user-friendly interfaces, they sometimes lack the personalized support of traditional banks. The reliance on automated systems and online resources can be efficient for straightforward transactions, but it can be a drawback when complex issues or disputes arise. Resolving a transaction error, for example, might involve navigating automated chatbots and online FAQs instead of direct interaction with a customer service representative.
Security and Regulatory Compliance: Emerging Challenges
The regulatory landscape for fintech is still developing. While established players like Zaro invest significantly in bank-level security protocols, understanding their specific licensing and regulatory oversight is paramount. South African businesses using fintech platforms should confirm that these providers comply with local KYC and AML regulations, ensuring a level of security comparable to established financial institutions. Moreover, as the fintech sector expands, staying informed about new regulations and their potential impact on transfers is vital for making informed and secure financial decisions.
Security and Regulation: What Actually Protects Your Money

When sending money abroad, security goes beyond just encryption and fraud prevention. It requires a deeper understanding of the regulatory landscape surrounding your chosen provider. This framework differs significantly between traditional banks, forex brokers, and fintech platforms, having a direct impact on the safety of your funds.
Banks: The Comfort of Familiar Regulation
South African banks operate under the watchful eye of the South African Reserve Bank (SARB). They adhere to strict international compliance standards, offering a high level of consumer protection. This includes maintaining specific capital reserves and complying with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. These measures provide assurance that your money is handled responsibly. Furthermore, established dispute resolution processes offer recourse should any issues arise.
This well-established structure makes banks a solid choice for those prioritizing regulatory oversight and established procedures.
Forex Brokers: Navigating the Regulatory Spectrum
South African forex brokers are regulated by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). However, the level of protection varies depending on the broker's specific license and adherence to these regulations. Reputable brokers maintain stringent compliance programs, including segregated client accounts and robust risk management procedures.
Before choosing a broker, verifying their FSCA authorization and understanding their specific compliance measures is critical. This due diligence can protect you from less scrupulous or unregistered entities. For those comfortable with a bit more research, a well-regulated forex broker can offer competitive exchange rates and specialized services.
Fintech Platforms: Innovation and Evolving Oversight
Fintech platforms often present innovative solutions for sending money abroad. Companies like Zaro prioritize security, employing measures such as two-factor authentication and encryption. However, the regulatory environment for fintech is still evolving.
Users should actively evaluate a platform's security practices, understanding the provided insurance coverage or guarantees. This is especially important with newer platforms or those operating in less established jurisdictions. Choosing an FSCA-licensed platform provides an added layer of security. Fintech platforms can offer a compelling blend of convenience and cost-effectiveness, but require users to be more proactive in assessing security.
Shared Responsibility: Your Role in Security
Ultimately, security is a shared responsibility. Providers must implement strong safeguards, but users also play a vital role. Choosing providers with transparent fee structures, clear terms of service, and verifiable regulatory compliance is paramount. By understanding the institutional and regulatory context of your chosen provider, you can confidently navigate the complexities of forex and protect your funds when sending money abroad.
Strategic Decision-Making: Matching Platforms to Real Scenarios
Sending money abroad requires a strategic approach. The "best" platform isn't a constant; it depends heavily on your individual needs and the specifics of the transfer. Let’s analyze some real-world examples to understand which platform shines in which situation.
Regular Family Remittances
Think small, recurring transfers – the kind you might send to family regularly. For these, fintech platforms like Zaro often present the most appealing blend of speed and affordability. Their digitally-focused design streamlines the process, minimizing both transfer times and fees. This efficiency is perfect for frequent, smaller amounts. Key considerations here are how easily your recipient can access the funds and whether the platform supports payout in their local currency.
Large Property Purchases or Investments
When the stakes are higher, like with international property purchases or significant investments, the security and compliance offered by traditional banks become paramount. While their fees might be higher, their established infrastructure and regulatory adherence provide a greater level of protection and recourse should issues arise. Furthermore, their advisory services can be invaluable when navigating the complexities of international financial regulations.
Emergency Transfers
Urgency changes the game. Imagine a sudden medical expense or family emergency abroad. Speed becomes critical, pushing fintech platforms back into the spotlight. However, consider the availability and accessibility of customer support in such stressful situations. Zaro and other fintechs provide digital support, but a traditional bank's telephone support might offer more immediate assistance during a crisis.
Business Payments
For businesses, especially those dealing with regular international transactions, forex brokers offer a specialized advantage. Their deep understanding of currency markets can unlock better exchange rates than those typically available through banks or fintech platforms. However, businesses must diligently research the broker's regulatory standing and compliance record to minimize potential risks.
The South African Context
South Africa’s outward remittance landscape presents its own set of considerations. While remittance inflows relative to GDP sit at 0.24% (World Bank data, 2020), South Africa primarily sends remittances, unlike many other African nations that are net receivers. Further details are available here. Transfers within the Common Monetary Area (CMA) are often simpler and cheaper than those going outside the CMA. Exchange rate volatility, especially for Rand-based transfers, becomes a critical factor, highlighting the importance of choosing a provider with transparent and competitive rates.
Adapting Your Approach
Your international money transfer needs are dynamic. As your financial situation evolves, your choice of platform should too. Regularly review your provider, ensuring it still aligns with your current transfer patterns and financial goals. This might mean transitioning from a fintech platform to a forex broker as your transaction volumes grow, or opting for a traditional bank when security is paramount for a high-value transfer. Staying informed and adaptable is key to maximizing efficiency, minimizing costs, and effectively managing the risks inherent in international money transfers.
Key Takeaways
This section offers a practical guide to navigating the complexities of foreign exchange when sending money abroad. We've distilled our analysis into actionable strategies, providing you with the tools to assess different platforms, recognize when switching providers is advantageous, and structure your international transfers for optimal efficiency. This includes tailored guidance for South African residents and practical tips for securing favorable exchange rates, regardless of your chosen platform.
The infographic below provides a simplified decision tree to help you choose the right transfer method based on the amount and urgency of your transaction.
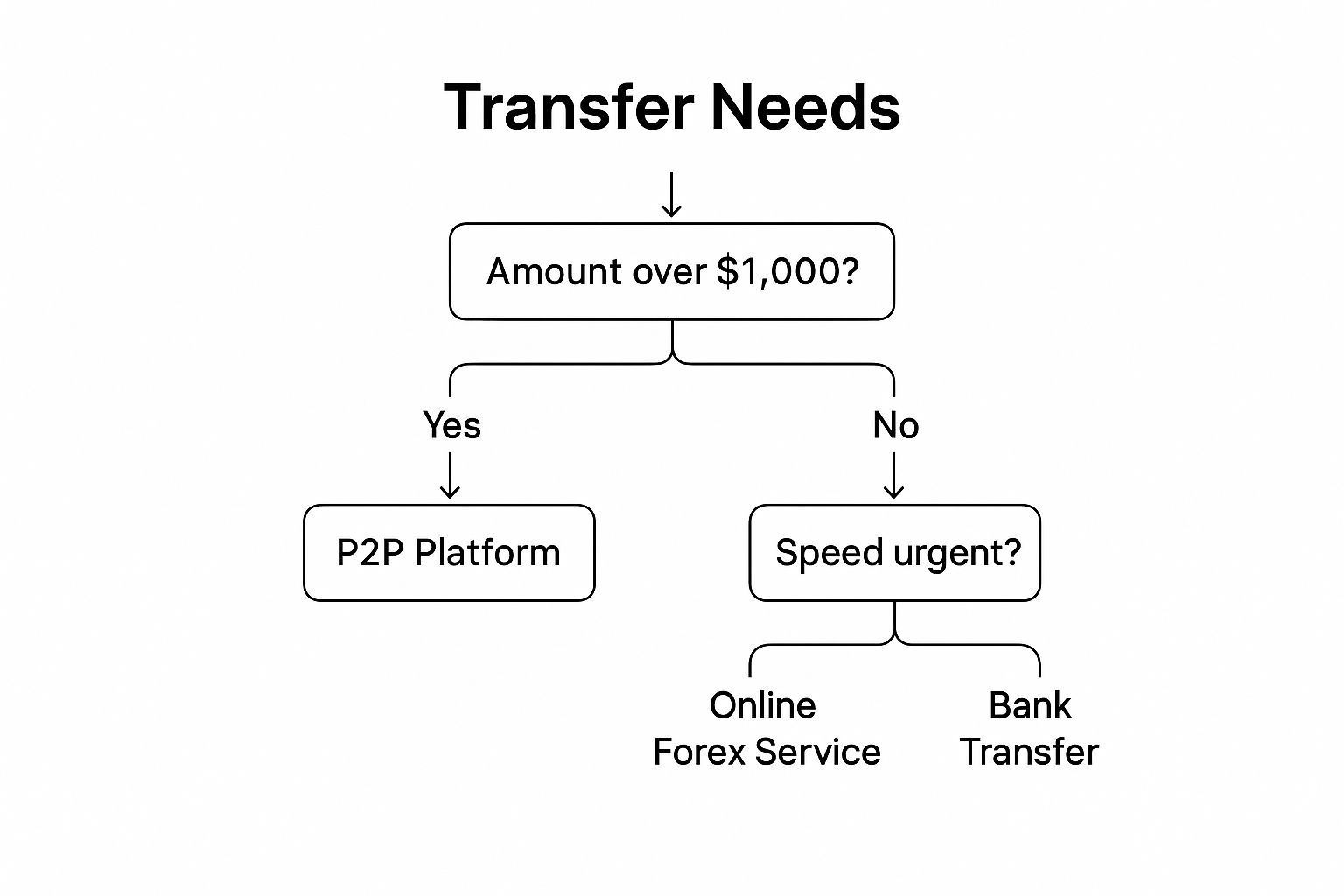
This decision tree highlights that for smaller transfers under $1,000 where speed is less critical, peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms often strike the best balance. Larger sums or time-sensitive transfers may benefit from online forex services or, for maximum security with substantial amounts, traditional bank transfers.
Practical Tips for South African Residents Sending Money Abroad
Negotiate Exchange Rates: Don't settle for the initial rate offered. Negotiating, particularly with banks and forex brokers, can often result in improved exchange rates.
Understand the True Cost: Look beyond the stated transfer fee. Inquire about correspondent bank fees, exchange rate margins, and any other charges that may apply.
Strategic Timing: Exchange rates fluctuate. Timing your transfer strategically can have a significant impact on the final amount received.
Compliance Matters: For larger transfers or business payments, prioritize providers with robust compliance frameworks and regulatory oversight.
Regular Review: Your needs evolve. Periodically re-evaluate your chosen platform to ensure it continues to align with your transfer activity and financial objectives.
Discerning Marketing Hype from Real Value
Many providers highlight speed and low fees, but often obscure the complete picture. Focus on the factors most relevant to your circumstances. Is it speed, cost, security, or a combination of these? Don't be swayed by marketing tactics. Prioritize transparent pricing, clear terms of service, and verifiable regulatory compliance.
Zaro: A Solution for South African Businesses
Zaro provides South African businesses with a transparent and efficient solution for managing international payments. By offering real exchange rates, zero spread, and eliminating SWIFT fees, Zaro removes hidden costs, simplifies transfers, and gives businesses greater control over their finances.
